Free Fall (time)
Tags | |
UUID | b4e3dc83-1c3e-11e6-9770-bc764e2038f2 |
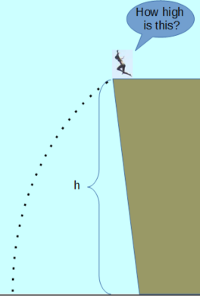
The Free Fall (time) calculator computes the duration of time that an object will be in free fall based on the height and the acceleration due to gravity.
INSTRUCTIONS: Choose units and enter the following:
- (h) This is the height of the free fall
Free Fall Duration (t): The calculator returns the time in seconds. However this can be automatically converted to compatible units via the pull-down menu.
The Math / Science
Time of Free Fall equation is meant for the context of free fall, or constant acceleration downwards due to Earth's gravity without rest, ignoring air resistance. Here, t is the time it takes for the object in question to fall a given distance (Height) with it's acceleration of g (the acceleration at sea level due to gravity, roughly 9.8 m/s^2).
The formula for the time of free fall is:
t=√2·hg
where:
- t is the time duration of a free fall
- h is the height of the free fall
- g is the acceleration due to gravity
 Free Fall Calculators
Free Fall Calculators
- Free Fall (time): Computes the duration of time that an object will be in free fall based on the height and the acceleration due to gravity.
- Free Fall (distance): Computes the distance that an object will be in free fall based on the duration of the fall and the acceleration due to gravity.
- Free Fall (Velocity at Impact): Computes the final velocity of an object after a free fall based on the height and the acceleration due to gravity.
- Free Fall (Energy on Impact): Computes the kinetic energy at impact based on the height of free fall, acceleration due to gravity and the mass of the object.
- Model Rocket Altitude: Computes the estimated maximum altitude of a rocket based the distance from the launch point and the angle to top point of flight (zenith).
- Object Height by Time to Drop: Estimates the height of an object based on the time it takes for an object to drop from the top of it.
- Elevation of Object (angles and separation): Computes the height of an object based on two angle measurements and the distance between them.
- Distance Traveled at Constant Acceleration: Computes the distance traveled by an object after a period of time, based on its initial distance from the origin, initial velocity and a constant acceleration.
- g (acceleration due to gravity at sea level): Acceleration due to Gravity (g) at sea level on Earth is 9.80665 m/s2.
Equations and Data Items
Calculators
Collections
- Comments
- Attachments
- Stats
No comments |

