Amplitude of a Wave
Tags | |
UUID | c3e7104c-e69d-11ec-8155-bc764e203090 |
The Amplitude of a wave equation computes the amplitude of a wave using the wave number(k), displacement of the wave(x), the angular frequency(), the time passed(t), and the phase angle().
INSTRUCTIONS: Choose units and enter the following:
- (y) Wave Displacement
- (x) Wave Distance
- (k) Wave Number (in rad/m)
- (w) Angular Frequency
- (t) Time
- (p) Phase Constant
Amplitude(A): The calculator returns amplitude(A) in meters. However, this can be automatically converted to other amplitude units via the pull-down menu.
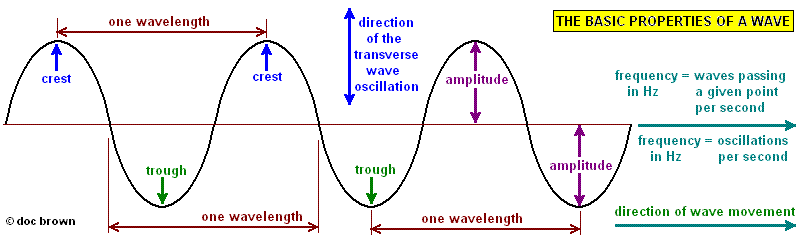 The Math / Science
The Math / Science
This equation comes from the basic wave equation:
where,
- y(x,t) are the parameters of the wave
- A is the amplitude
- k is the wave number
- x is the wave distance
- w is the angular frequency
- t is the time passed
- is the phase angle.
Some simple Algebra allows us to gain the equation that you see at the top of the page:
Notes:
Please enter the wave number in the units of radians-per-meter as it won't compute properly in different units.
References:
- Comments
- Attachments
- Stats
No comments |
This site uses cookies to give you the best, most relevant experience. By continuing to browse the site you are agreeing to our use of cookies.
