Transformer Design Collection
The equations, constants, calculators and collections shown below are all related to the design of a transformer.
See the many related electrical equations in vCalc's Electrical Library.
What is a Transformer
A transformer transfers electrical energy between electrical circuits through electromagnetic induction. Electromagnetic induction produces an electromotive force, the force that drives a current in a conductor when the conductor is exposed to time varying magnetic fields.
Transformers are used to increase or decrease the alternating voltages in electric power applications, thus they "transform" the voltage from one voltage level to another voltage level.
A varying current in the transformer's primary winding creates a varying magnetic flux in the transformer core and a varying field impinging on the transformer's secondary winding. See Figure 1
Varying magnetic field in a conductor causes motion of charge thus inducing voltage in the conductor. In the transformer varying magnetic field at the secondary winding induces a varying electromotive force (EMF) or voltage in the secondary winding due to electromagnetic induction.
In other words, the varying current in the primary winding creates varying magnetic field in the secondary winding and that, in turn creates voltage in the secondary winding.
Since we distribute power over large distances using high voltage alternating current delivery wires, it is necessary to step the voltage down when it arrives at your home. Thus transformers play an essential part in residential power delivery, among a myriad of other uses.
Transformer Design Elements
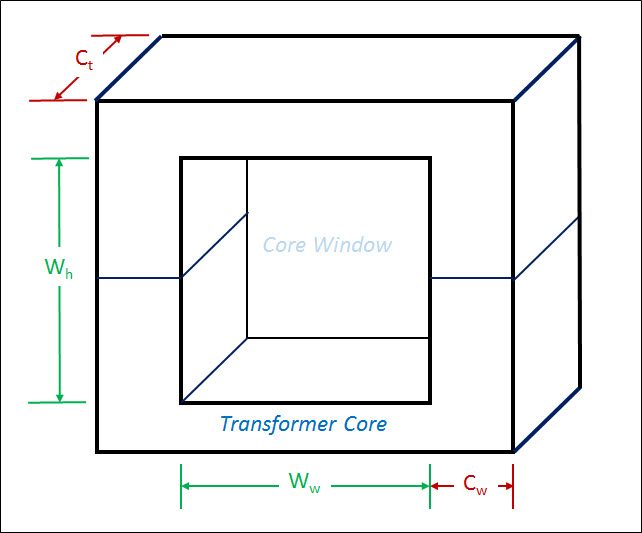
Figure 2 shows the dimensions of a simple transformer's core design. The Core is the component of the transformer in which the magnetic flux is concentrated and around which the winding from from the primary and secondary circuits are wound. The Core Geometry is a key transformer design element and is expressed in units of `"cm"^5`.
Equations
- Transformer Core Geometry - Kg Use Equation
- Magnetic Flux Density Use Equation
- Flux Density from Field Strength Use Equation
- Magnetic Flux Unit Conversion Use Equation
- Magnetic Flux Density Unit Conversion Use Equation
- Coil Magnetic Energy Use Equation
- Stored Magnetic Energy (Volume) Use Equation
- Magnetic Field (solenoid) Use Equation
- Stored Magnetic Energy Use Equation
- Phase Angle (AC) Use Equation
- Power Factor Use Equation
- Peak Voltage Use Equation
- Inductance per unit length Use Equation
- Inductance of a coil Use Equation
- Relative Permittivity Lookup Use Equation
- Inductance for a Solenoid Use Equation
- Transformer Design - Core Size Use Equation
- DC Resistance of a Wire Use Equation
- Power Loss Due to Wire Resistance Use Equation
- Winding Porosity Use Equation
- Transformer Design - Impedance Matching Use Equation
- Transformer Window Utilization Factor Ku Use Equation
- Transformer Electrical Magnetic Operating Factor Ke Use Equation
- vVoltage Use Equation
- vElectric Charge Use Equation
- Electric Field Intensity Unit Conversion Use Equation
- V (Ohm's Law) Use Equation
- Voltage from Current and Power Use Equation
- Voltage from Current and Resistance Use Equation
- Resistance from Power and Potential Use Equation
- Power from Voltage and Resistance Use Equation
- Voltage using angular velocity Use Equation
- Time Averaged Power (V,R) Use Equation
- Time Averaged Power (V, I) Use Equation
- Electric Current Unit Conversion Use Equation
- Capacitance Unit Conversion Use Equation
- Energy Density of Magnetic Field Use Equation
- Magnetomotive Force Use Equation
- Magnetic Field Use Equation
- Flux Density[mu,H] Use Equation
Data Items
- Magnetic Flux Quantum (emag) Use Data Item