Weight of Rebar in Grid
The Weight of Rebar in a Slab calculator computes the total weight 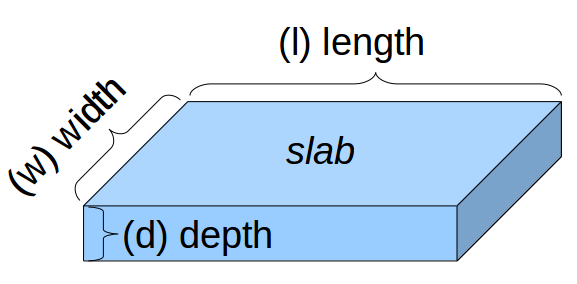
 Concrete Slab with one Rebar Grid mat of reinforcement bars (rebar) needed for a concrete slab based on the dimensions of the slab and the spacing and size of the rebar.
Concrete Slab with one Rebar Grid mat of reinforcement bars (rebar) needed for a concrete slab based on the dimensions of the slab and the spacing and size of the rebar.
INSTRUCTIONS: Choose units and enter the following:
- (L) Slab Length
- (W) Slab Width
- (rS) Rebar Size (choose from list)
- (oC) on-center spacing of the rebar (default: 18")
- (i) Inset, distance from the side of the slab to the rebar grid (default: 3").
- (m) Number of Mats
- (OC) The output choice of weight (default) or length.
- (rL) Length of Rebar Sticks (bars being used before they are cut). Common lengths are 20, 30, 40 and 60 feet.
- (LF) Lapping Factor 40 (default) and 60 are common.
Weight of Rebar: The calculator returns the total weight of the rebar in pounds. However, this can be automatically converted into other weight units (e.g. kilograms or tons) via the pull-down menu. If OC set to length, the length of the rebar in the mat(s) is return in feet, which can be automatically converted to other length units (e.g. meters or yards) via the pull-down menu. See the Rebar Calculator for more concrete and rebar functions and features. See VIDEO INSTRUCTION for a YouTube video on the use of this calculator.
The Math / Science
Rebar is short for "Reinforcement Bars". Rebar is often used inside concrete for added strength, including use in common slabs. This formula provides a length and weigh rebar calculation that is useful in understanding the additional load of the slab added by the rebar steel. It is also useful for calculating the weight of rebar for rebar expense and when considering transport. Steel is dense and heavy. Most vehicles would be considerably overloaded in weight of rebar long before their potential volume is full, which poses a significant safety issue. In the U.S., most pickup trucks are rated at a half or three quarters ton load rating. This rating indicates the safe weight of a load that can be carried. The rebar weight formula can help determine how many trips are required to transport the load of reinforcement steel safely.
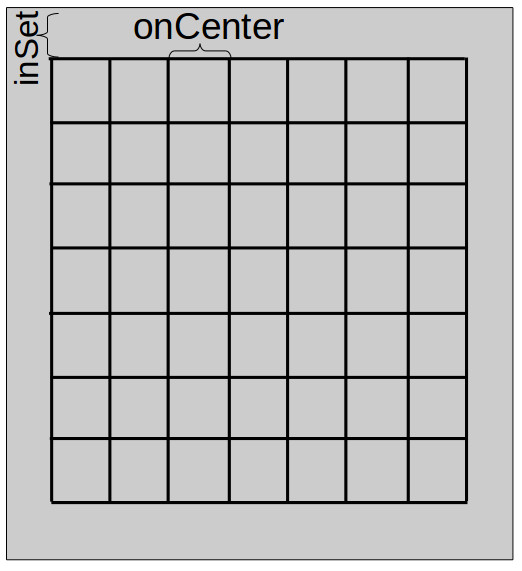
The rebar weight algorithm calculates the weight of reinforcement steel bars in a concrete slab. The algorithm calculates the area of the slab, and calculates the length of rebar needed for a rectangular grid within the slab. The grid is specified by the inset from the edge of the slab and the nominal separation between horizontal and vertical rows of rebar (onCenter - see diagram). Once the algorithm calculates the length of rebar, the length is used with the user specified rebar size, and density constants from the vCalc library to calculate the total weight of the reinforcement steel bars.
The user specified parameters are:
- (L) Length - length of the slab
- (W) width - width of the slab
- (rS) size - this is the size of the rebar. The standard sizes include: 2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,7 ,8 ,9 ,10 ,11 ,12 ,14, 16, 18, 20
- (oC) OnCenter - the on-center spacing between rebar, which defaults to 18"
- (i) inset - an offset distance from the side of the slab to the first row the rebar grid, which has a default of 3"
- (m) mats - this is the number of mats (layers of grids) of rebar.
- (OC) Output choice - this lets the user choose between the weight of the rebar in the grid or the length of rebar in the grid.
- (rL) Rebar Length - this is the length of the rebar sticks used in constructing the rebar grid.
- (LF) Lapping Factor - this the multiple of the rebar diameter used to define the overlap length at rebar joints (extension).
The calculation determines the need for an extra rebar using an internal tolerance for for a spacing fraction that exceeds the tolerance with a default of 1".
General Rebar Information
Rebar is short for reinforcing bar. Rebar is a roughly circular steel bar with ribs used to provide added tensile strength to concrete structures. Rebar is put in place before concrete is poured. When the concrete has hardened, the concrete around the rebar ribs keep the rebar in place. Rebar and concrete expand similarly with temperature variations. This all has the net result of substantially added tensile strength when rebar is part of the concrete form. Carbon steel is the most commonly used material for rebar, which may also be coated with zinc or epoxy resin.
Rebar is laid out in grids, crisscrossed patterns of rebar, tied at the intersections where runs of rebar touch. The grids have spacing between the rebar rows, and they are placed within the concrete form by a specified inset from the edge of the concrete. Multiple parallel grids, at uniform space intervals, are referred to as rebar mats.
Rebar Terms
- Rebar - reinforcing steel bar.
- Stick - one length of rebar. In the U.S., the most common lengths of rebar sticks are 20', 40' and 60'.
- Lapping - when two sticks of rebar are overlapped and bound together.
- Lapping Factor - the multiple of a rebar diameter used to specify appropriate rebar lapping length.
- Mat - a crisscross grid of rebar sticks. There may be more than one mat with space in between mats.
- Size - the indicator of the diameter of rebar sticks. Note: guage is not a correct term for rebar.
Rebar Size
In the United States, rebar sizes are in increments of 1/8th inches in diameter. Therefore, size 4 is 4/8th of an inch, which is 1/2", and size 8 is a full inch in diameter. Based on this and the density of steel used in rebar, the Rebar Size Table contains reasonably accurate specifications of rebar linear weight and lateral (face) area based on rebar size.
Rebar Lapping
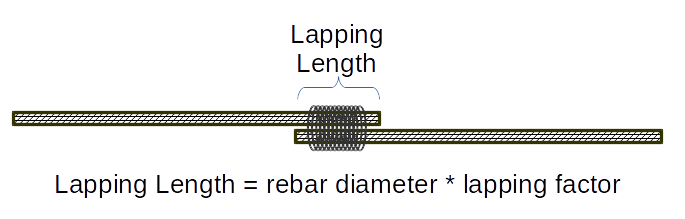
The most common lengths of pre-cut rebar in the United States are 20`, 40' and 60'. These are known as rebar sticks. When the dimensions of a slab, wall or other form exceed the length of a single stick of rebar, it is required to rebar lapping length. The length of the lap is specified by a "Lapping Factor (LF)" which is often 40 or 60 times the diameter of the rebar. Engineering specifications of a lapping factor should always be applied.
Rebar Tools
A class of rebar tools, both powered and manual, have been developed to aid construction workers in working with rebar. These include the following:
- Rebar Cutters are used to cleanly and safely cut sections of rebar.
- Rebar Benders are used to bend rebar sticks precisely to fit into concrete forms.
- Rebar Tiers are used to tie rebar grid intersections and for rebar lapping.
Rebar and Slab Calculators:
- Rebar Calculator (Spanish Version: Calculadora de Barras de Refuerzo)
- Weight of Any Volume of Concrete
- Rebar and Concrete Volume and Weight in a Slab
- Rebar Weight
- Length of Rebar needed for a slab.
- Weight of Rebar in a slab.
- Weight, Volume of Concrete and Surface Area of a Concrete Slab
- Surface Area of a slab
- Surface Area of Concrete Forms.
- Volume of Concrete in a slab.
- Water Needed for Concrete
- Rebar and Concrete in a Slab
- Length of Rebar in Grid
- Weight of Rebar in Grid
- Rebar in a Wall
- Rebar in an Irregular Shaped Slab
- Rebar in a Circular Slab
- Rebar Lapping Length
- Rebar Cost Estimate
- Weight of Length of Rebar
- Concrete Displaced by Rebar
- Total Weight of a Slab with Rebar
Masonry Calculators
- Total Slab Weight - This includes the weight of the rebar and the concrete.
- Brick or Block Wall - Number of brick or block needed for a wall.
- Foundation - Poured - Amount of concrete needed for a poured foundation.
- Foundation - Block - Number of blocks needed for a foundation.

