Angle of Vector (||, )
vCalc Reviewed
The Vector Angle equation computes the angle, , of a vector from the magnitude of the angle, || and the y-component of the vector, vy. See Figure B.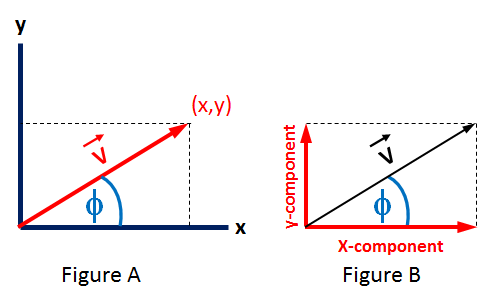
INSTRUCTIONS: Enter the following:
- (|| ) Vector Magnitude
- (vy) Vertical Vector Component
Vector Angle (): The calculator returns the angle in degrees. However, this can be automatically converted to compatible units via the pull-down menu.
3D Vector Functions
- k V - scalar multiplication
- V / |V| - Computes the Unit Vector
- |V| - Computes the magnitude of a vector
- U + V - Vector addition
- U - V - Vector subtraction
- |U - V| - Distance between vector endpoints.
- |U + V| - Magnitude of vector sum.
- V • U - Computes the dot product of two vectors
- V x U - Computes the cross product of two vectors
- Vector Angle - Computes the angle between two vectors
- Vector Projection - Compute the vector projection of V onto U.
- Area between Vectors - Computes the area between two vectors
- Vector Rotation - Compute the result vector after rotating around an axis.
- (ρ, θ, φ) to (x,y,z) - Spherical to Cartesian coordinates
- (x,y,z) to (ρ, θ, φ) - Cartesian to Spherical coordinates
- (r, θ, z) to (x,y,z) - Cylindrical to Cartesian coordinates
- (x,y,z) to (r, θ, z) - Cartesian to Cylindrical coordinates
Reference
Young, Hugh and Freeman, Roger. University Physics With Modern Physics. Addison-Wesley, 2008. 12th Edition, (ISBN-13: 978-0321500625 ISBN-10: 0321500628 ) Pg 16 eq 1.6
This equation, Angle of Vector (||, ), is used in 2 pages
Calculators
Collections
- Comments
- Attachments
- Stats
No comments |
This site uses cookies to give you the best, most relevant experience. By continuing to browse the site you are agreeing to our use of cookies.
