Cost of Electricity
Tags | |
UUID | b80b425e-191a-11e5-a3bb-bc764e2038f2 |
The Cost of Electricity calculator computes the cost of consuming an amount of power over a period of time at a given utility cost.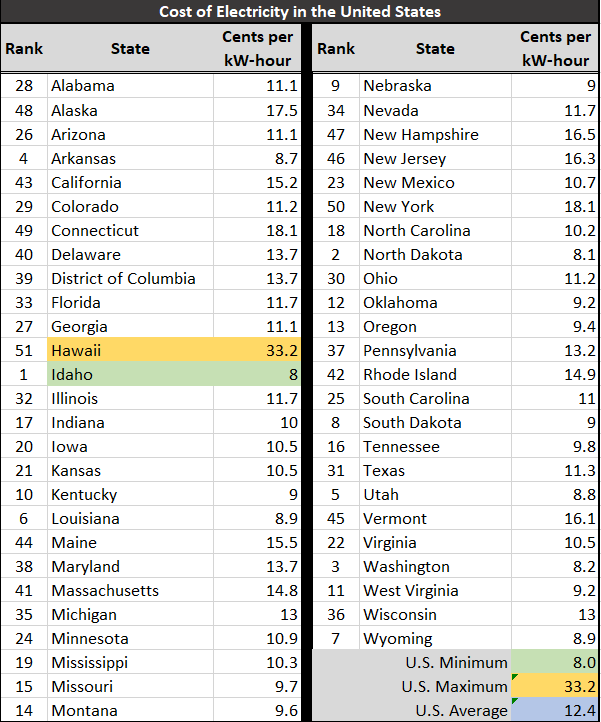
INSTRUCTIONS: Choose units and enter the following:
- (P) Average Power usage
- (T) Time the power is being used (consumed)
- (UC) Unit Cost of power (Utility cost for a kiloWatt-hour)
Cost of Electricity (TC): The calculator returns the cost in U.S. dollars. However, this can be automatically converted to other currency units via the pull-down menu.
The Math / Science
The Cost of Electricity calculator uses the average power usage, duration of usage and cost per power unit to compute the cost of electricity. The formula for the Cost of Electricity is:
TC=P⋅T⋅UCTC=P⋅T⋅UC
where:
- TC = Total Electric Cost
- P = Average Power Use for appliance (e.g. 60 watt light bulb)
- T = Time of consumption
- UC = Unit Cost of power
This calculator answers questions like the following:
- If I operate a 60 watt light bulb for 3 months, how much will it cost in electricity.
- How much does it cost to operate a sump pump (at 1,050 watts) for three days?
- How much does it cost to run an air conditioner (at 1,300 watts) for one month?
Note: The currency conversions in vCalc are updated every five minutes. Using this, you can enter the power rates in the local currency, and see what that costs in your currency (e.g. electricity costs X per kilowatt hour in Great Britain Pounds (GBP), but what does that power cost equate to in Japanese Yen.)
General Information
Utility cost vary by provider and location. Check your monthly power bill to see the rate that applies to you. A recent survey indicated that the average rate for a kiloWatt-hour in the United States was 11.88 cent per kWh (2012)
The Don Rowe website provides an estimated power (watts) level for different appliances, tools, pumps and air conditioners HERE.
The U.S. averages come from U.S. Energy Information Administration
Electrician Calculators
- Voltage Drop: This computes the voltage drop in volts and as a percentage over a length of cable (wire) based on length of wire, gauge, wire material, temperature range and phase.
- Wire Gauge Choice for Safe Voltage Drop: This determines the lightest gauge of wire that can be used over a run (circuit) that maintains adequate voltage.
- Circular Mils and Voltage Drop: This computes voltage drop based on wire diameter in circular mils instead of wire gauge.
- Electricity Usage Cost: This computes the cost of electricity for the use of a piece of equipment based on the power consumption rate, duration and cost of electricity.
- Electricity Consumption: This computes the amount of electricity consumed by an electrical appliance or motor over time.
- Rolling Offset: This computes the travel (T) and run (R) of a rolling offset used in conduit piping based on the offsets and angles.
- Diameter of AWG Wire: This provides the diameter of wire based on the American Wire Guide (AWG) gauge in mils and millimeters, and it also provide the cross-section area in square millimeters.
- P = V2 / R: This computes power (Watts) based on the voltage (V) and resistance (R).
- DC to AC Converter: Computes the approximate voltage of Alternating Current (AC) from the voltage of Direct Current (DC).
- Diameter to Circular Mils: Computed the circular mils of a wire and the cross-section area based on the wire's diameter.
Collections
- Comments
- Attachments
- Stats
No comments |

