Polygon Slab Surface Area
The Surface Area of a Polygon Slab calculator computes the area of a regular polygon slab with n sides (e.g. n=5 for a pentagon, 6 for a hexagon, 8 for an octagon etc) using the radius (r) from the center of the slab to any one of the vertices.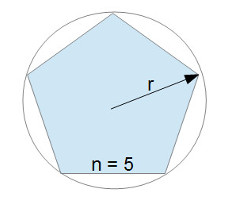 Polygon (pentagon) slab
Polygon (pentagon) slab
INSTRUCTIONS: Enter the following:
- (n) Number of Sides in Polygon slab (e.g. 7 heptagon)
- (r) Radius of Polygon
Area of Polygon Slab (A): The calculator returns the area in square feet. However, this can be automatically converted to compatible units via the pull-down menu.
The Math / Science
This calculation can be used to fit a polygon shaped object (concrete slab, deck, porch, gazebo, etc) in a defined space. Since the polygon whose surface area we are calculating here is defined by a radius to the circle that passes through the vertices of the polygon, you can fit the polygon into any space that will contain that circle of radius r.
So measure an area to have at minimum length and width equal to or greater than the diameter of the circle and the polygon defined by the radius r will fit in this space. And you will know the total area of the polygon space.
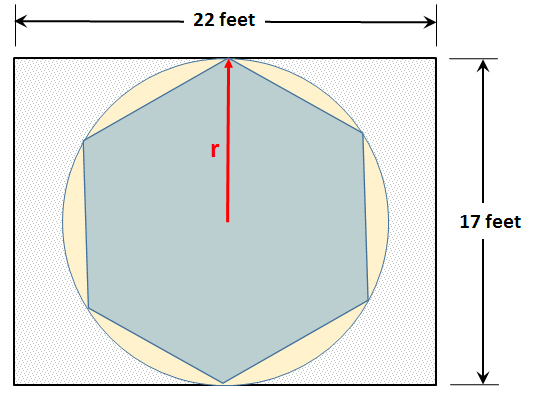
Example: A homeowner wishes to put a hexagonal concrete patio slab in a corner of their garden on which they will places some comfortable outside furniture. They want to place the slab centered in a section of the garden where there is a 22 foot by 17 foot open space. They want to make the patio slab as large as possible with its hexagon vertices spanning the center line. And finally, they want to know how many square feet of surface space this hexagon patio provides so they can talk knowledgeably to the supplier of outdoor furniture in making a selection of furniture that will fit comfortably on their new patio.
In the picture to the right, the circle which touches both sides of the rectangular area is the largest circle that would fit in the 22 foot by 17 foot section of the garden. The radius aligned along the center line is half the width of the area: 8.5 feet and the hexagon has number of sides, n = 6.
And thus this equation for the area of a polygon slab tells us the largest slab that will fit the space and be aligned this way will have a surface area:
AreaSlabAreaSlab = 192.15 ft2ft2
Polygon Shaped Slab Calculators
Polygon Slab Surface Area: Computes the surface area of a regular polygon slab.
- Polygon Slab Side Length: Computes the length of the individual sides a regular polygon slab.
- Polygon Slab Cost: Computes the cost of concrete in a polygon shaped slab.
- Polygon Slab Perimeter: Computes the perimeter of a polygon shaped slab.
Masonry Calc (Concrete, Brick and Block, Rebar)
The MASONRY suite includes collections of functions associated with product estimations on projects done with brick, block, concrete and rebar.
Concrete Slab Calculators
The following functions apply to estimating the amount of concrete, rebar, form boards and water needed for concrete slabs of different shapes: rectangular with squared corners, circular including semi-circle, and polygon shapes from triangular up (e.g., pentagon for 5 sides and dodecagon for 12 sided polygon).
Rectangle Slab
- Rebar and Concrete in a Slab: Computes the total length and weight of rebar and the volume and weight of concrete needed for a rectangular slab, taking into account the concrete displaced by the rebar.
- Concrete in Rectangle Slab: Computes the volume of concrete in a rectangle (squared corners) slab based on the dimensions. It includes the volume of concrete in cubic yards and the equivalent volume in bags of concrete. It also includes the surface area, length of form boards, and the water requirement.
- Slab Weight: Computes the weight, volume of concrete and surface area of a rectangle slab based on the length, width and depth of the concrete of the slab and the density of concrete.
- Weight of Slab with Rebar: Computes the weight of a rectangle slab with rebar based on the length, width and depth of the concrete of the slab, the density of concrete and the size and spacing of rebar. It includes total weight (concrete and rebar), and the contribution of weight from rebar and concrete separately.
- Slab Area and Perimeter: Compute the surface area and perimeter of a rectangular slab based on the dimensions.
Circular Slab
- Volume of Circular Slab: Computes the slab surface area, perimeter and cubic yards of concrete in a circular slab based on the diameter and depth. It also provides, the equivalent volume in 80lb, 60lb and 40lb bags of concrete and the water requirement.
- Circular Slab Weight: This computes the weight of the concrete in a circular slab based on the diameter, depth and density of concrete.
- Rebar and Concrete in a Circular Slab: This computes the length and weight of rebar in a rectangular slab. It also computes the total weight of the slab including concrete, taking into account the concrete displaced by rebar.
- Semi-Circle Slab Volume: Computes the volume of concrete needed for a semi-circular slab based on the radius and depth.
- Semi-Circle Slab Weight: Computes the weight of concrete in a semi-circular slab based on the radius, depth and density of concrete.
Polygon Slab
- Concrete in Polygon Slab: Computes the surface area and cubic yards of concrete for a polygon slab based on the dimensions and depth. It also provides the equivalent volume of concrete in 80lb, 60lb and 40lb bags of concrete.
General Functions
- Concrete Weight: Computes the weight of a specified volume (e.g., 2.3 cubic yards) of concrete.
- Price of Delivered Concrete: Computes the price of delivered concrete based on the volume, price per cubic yard, pumping cost, delivery distance, and mileage.
- Water Needed for Concrete: Compute the amount of water needed to make a volume of concrete.
- Concrete Displaced by Rebar: Computes the volume of concrete displaced by a length of rebar based on the length and size of rebar.
Masonry Walls (Brick, Block, Mortar Joints)
- Brick or Block Wall: Computes the number of brick or block needed for a wall based on dimensions.
- Bricks or Blocks in a Wall
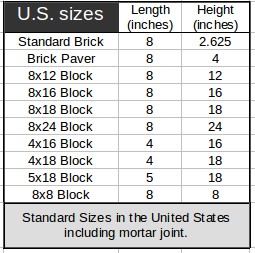 : Computes the number of standard U.S. brick or block needed for a wall using feet and inches.
: Computes the number of standard U.S. brick or block needed for a wall using feet and inches. - European Brick or Block in a Wall
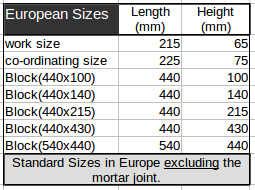 : Computes the number of standard European bricks or block in a wall using meters and centimeters.
: Computes the number of standard European bricks or block in a wall using meters and centimeters. - Custom Stone in a Wall: Computes the number of masonry units (stone, block or stone) in a wall based on the dimensions of the wall and the dimensions of the units and the thickness of the mortar joints. It also returns the number of rows needed and the number of stone per row.
- Concrete, Rebar and Forms for Wall: Computes the volume of concrete, amount of rebar and the surface area of forms for a concrete wall.
Foundations - Footers - Piers
- Blocks in a Foundation: Computes the number of blocks needed for a foundation based on the dimensions of the foundation and the size of the blocks with a standard size mortar joint.
- Concrete in a Poured Foundation
: Compute the volume of concrete, the square feet of the forms and the number of 4'x8's needed for the forms.
- Concrete in a Footer: Computes the volume of concrete for a footer based on the length, width and depth of the footer.
- Concrete in a Footer (Cross Section): Computes the volume of concrete for a footer based on the length and cross-section area of a footer
- Concrete in a Pier: Computes the volume of concrete in a circular pier based on the radius and depth of the pier.
- Piers for a Building: Computes the number of piers and volume of concrete need for the piers of a building (e.g., pole barn) base on the building dimensions, pier spacing, diameter and depth.
- Concrete around Circular Post: Computes the volume of concrete around a number of round posts in a round hole based on the size of the hole and dimensions of the post.
- Concrete around Square Post:
Computes the volume of concrete around a number of square post (e.g., 6x6) in round hole based on the dimensions of the post, depth and width of the round hole.
- Comments
- Attachments
- Stats
No comments |

