Basic Stress and Strain Calculator
The stress and strain calculator calculates the elasticity of objects and material brought about by stress and strain forces.
Definition:
Stress is the magnitude of force that causes the deformation of an object or material.
Strain is the effect of deformation that has happened to an object.
Deformation is a change of shape due to an application of force on an object.
Stress
Stress formula is force applied to a surface called Pascals (Pa) calculated as newtons per unit surface area : Pa = N/m2
Types of stress:
- Tensile stress is caused when forces pull an object causing it to elongate
- Compression stress is caused when forces push on an object causing it ti contract
- Bulk stress is caused when an object is been squeeze by force from all its sides.
- Shear stress is the force that acts parallel to the cross sectional area of an object.
Strain
Strain is given in a fraction changing in:
- Length under tensile stress
- Volume under bulk stress
- Geometry under shear stress
Elasticity Modulus
It is the ratio of stress provide it does not exceed the elasticity limit, to the corresponding strain.
It is calculated as : stress/strain.
Types of Elastic Modulus.
There are three types of elasticity moduli.
Young Modulus(Y).

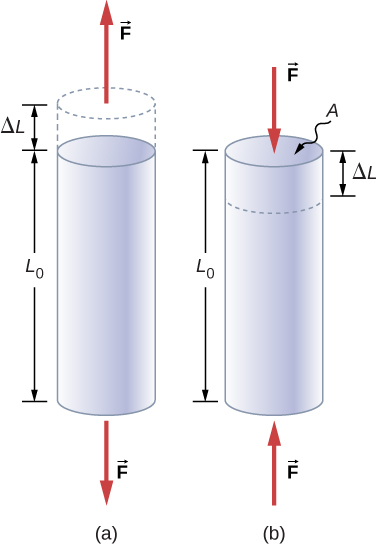
Young's Modulus is the elastic Modulus in relation to tensile stress and compression stress.
Consider a rod of length L0 and a cross sectional area A being stretched or compressed by a force F to form a new length L. When L is larger than L0 (a) it is elongated and when L is shorter than L0 (b) it is compressed.
Stress = F/A Strain = ∆L/L0
Y = (F/A) ÷(∆L/L0)
= (F /A )(L0 /∆L)
Bulk Modulus (K)
It is a constant that describes how resistant an object or material is under pressure. This changes the volume without changing the shape.
Bulk stress is referred to as pressure where Pressure = F/A. it is the increase in pressure ∆P over the normal pressure P0.
Bulk strain is measured in relation to the fractional change in volume.
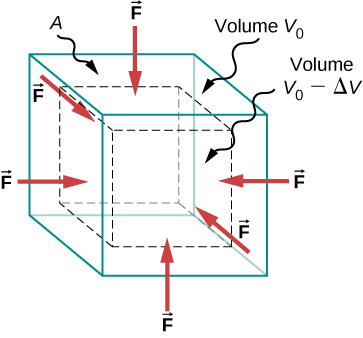
Formula: B = —∆P÷(∆V/V0)
= — ∆P(V0/∆V)
The minus(-)sign is necessary because an increase in pressure results to a decrease in volume which is positive and a decrease in pressure results to an increase in volume which is a negative.
Compressibility is the reciprocate of bulk modulus denoted as : β = 1/B.
Shear Modulus.
It is the deformation that occurs when two anti parallel forces of equal magnitude are applied tangentially to opposite surfaces of an object or material. It only concerns solid objects and materials.
It is the ratio of shear stress over shear strain.
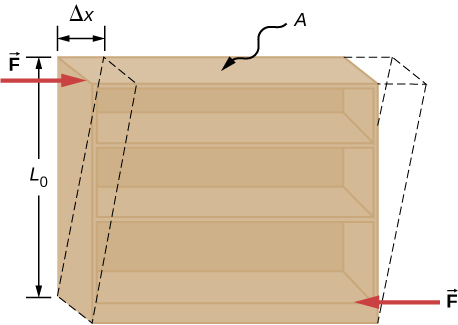
Shear strain is defined as the length of deformation at its maximum ∆x over the perpendicular length L0 of an object.
γ = ∆x/L0
shear stress=F∥/A.
S = (F∥/A)÷(∆x /L0 )
=(F∥/A)(L0 /∆x)
- ^ Fundamentals of Engineering. 8th edition, 2nd Revision. National Council of Examiners for Engineering and Surveying (NCEES) - 2001. ISBN 978-1-932613-59-9. pg 33
-
Ling, S. J., Sanny, J., & Moebs, W. (2016, September 16). 12.3 Stress, Strain, and Elastic Modulus. OpenStax. Retrieved November 16, 2021, from https://openstax.org/books/university-physics-volume-1/pages/12-3-s
-
Elert, G. (n.d.). Elasticity –. The Physics Hypertextbook. Retrieved November 15, 2021, from https://physics.info/elasticity/
Equations and Data Items
- Comments
- Attachments
- Stats
No comments |
