Distance - constant velocity
vCalc Reviewed
dx=x0+v0⋅t
Tags | |
UUID | 63cf8d3c-0d14-11e4-b7aa-bc764e2038f2 |
The Distance - Constant Velocity calculator uses the equation, dx= x0+v0⋅t, to compute the total linear displacement (distance travelled).
INSTRUCTIONS: Choose the preferred units and enter the following;
- (x0) This is the initial displacement.
- (v0) This is the initial velocity.
- (t) This is the duration of the motion or travel.
Distance: The calculator returns the distance in meters. However, this can be automatically converted to other length or distance units via the pull-down menu.
The Math / Science
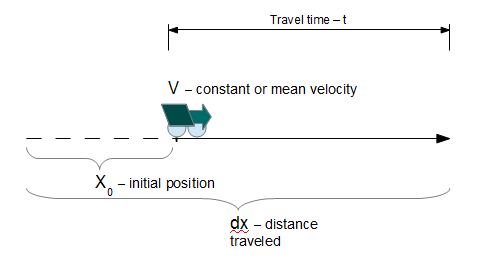 Motion under Constant Velocity
Motion under Constant Velocity
This calculator computes the distance an object travels as a function of time traveling at a constant initial velocity with the addition of an initial displacement (distance). This equation ignores external forces and so the object continues its motion at its initial constant velocity, v0, as an expression of Newton's First Law.
where:
- v0 - Initial velocity at time t = 0
- x0 - initial displacement at time t = 0
- t - time of travel in the x-direction
Vehicle Calculators
- Approach (Departure) Angle: Computes the maximum angle of a ramp onto which a vehicle can climb without scraping.
- Degree to Percent Grade: Converts a grade to a degree angle.
- Camber angle - Wheel camber (tilt) calculation of angle
- Camber offset - Wheel camber (tilt) calculation of offset
- Breakover Angle: Compute maximum angle that a vehicle can drive over without the ground touching the vehicle's undercarriage.
- Time to Overtake: Computes the time for one object to overtake another.
- Distance to Overtake: Computes distance traveled to overtake another.
- Speed to Overtake: Computes the average velocity to overtake another.
- Distance Traveled: Computes the distance traveled over a period of time.
- Speed from Skid Marks: Estimates the speed of a vehicle based on length of skid marks.
- Braking Distance: Estimates distance to stop a vehicle based on initial velocity and braking coefficient.
- Total Stopping Distance: Computes the distance to stop a vehicle based on the initial velocity, reaction time and a braking coefficient.
- Speed from the Braking Distance: Estimates the initial speed based on the distance to stop a vehicle and the a braking coefficient.
- Used Car Price Comparison: Estimates the better value between two vehicles based on their mileage, cost and expected lifespan (miles).
- Belt Length: Computes the length of a belt that goes around two pulleys based on the pulley diameters and the distance between the axles.
- Belt Speed: Computes the speed at which a linear length of belt travels around a pulley based on the diameter of the pulley and the rotation rate.
- Pulley RPMs: Computes the RPMs of a pulley based on the belt speed and diameter of the pulley.
- 2nd Pulley RPMs: Computes the RPMs of a second pulley based on the the RPMs and Diameter of the first pulley and the diameter of the second pulley.
- 2nd Pulley Diameter: Computes the diameter of a second pulley based on the RPMs and diameter of the first pulley and the RPMs of the second pulley.
- RPM of 4th pulley on three shafts: Computes the RPMs (rotation rate) of a pulley when the RPM and Diameters are known for a series of pulleys on three axles.
- 2nd Gear RPM: Calculates the RPMs of a second gear when the RPMs and number of teeth are known for the first gear and the number of teeth of the second gear is known,
- 2nd Gear Torque: Calculates the torque of a second gear when the torque and number of teeth are known for the first gear and the number of teeth of the second gear is known,
Motion Calculators:
- Compute Duration (Time) of Free Fall
- Compute Distance (Height) of Free Fall
- Compute Final Velocity of a Free Fall
- Compute the time from the distance and velocity.
- Compute the velocity from the distance and time.
- Compute the distance from the velocity and time.
- Distance from initial displacement, velocity and time
- Distance from initial displacement, velocity, time and constant acceleration
Reference
- Young, Hugh D., Roger A. Freedman, A. Lewis Ford, and Francis Weston Sears. "2.4." Sears and Zemansky's University Physics: With Modern Physics. San Francisco: Pearson Addison Wesley, 2004. 51. Print.
This equation, Distance - constant velocity, is used in 6 pages
Calculators
- Comments
- Attachments
- Stats
No comments |
This site uses cookies to give you the best, most relevant experience. By continuing to browse the site you are agreeing to our use of cookies.

