The Distance Traveled at Constant Acceleration calculator computes the distance traveled (dx) by an object after a period of time (t), based on its initial distance from the origin (x), the object's initial velocity (V) and a constant acceleration (a).
INSTRUCTIONS: Choose units and enter the following:
- (x0) Initial Displacement
- (V0) Initial Velocity
- (a) Constant acceleration
- (t) Duration of Travel
Distance(dx): The calculator returns the distance traveled in meters. However, this can be automatically converted into other length or distance units via the pull-down menu.
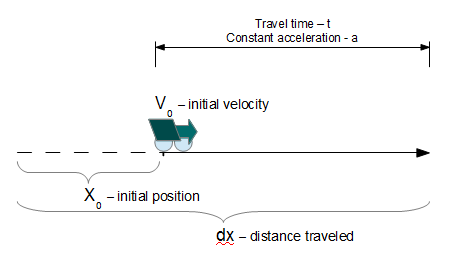 distance traveled a.k.a. displacement
distance traveled a.k.a. displacement
The Math / Science
The formula for the distance traveled with constant acceleration is:
dx = x+v⋅t+½⋅a·t²
where:
- dx is the distance traveled under constant acceleration
- x is the initial distance
- v is the initial velocity
- a is the constant acceleration
- t is the time of travel.
Application
A common application for this equation is the travel associated with the free fall of an object under the force of gravity. In the case of Earth's gravity, the constant acceleration is approximately 9.80665 m/s2. Note that this formula does not include other forces such as drag.
Calculus
Note, the first derivative of this equation with respect to time is:
`dx/dt = a*t + v`
Since dx/dt represents change in distance over time, which is the definition of velocity, the formula could read:
`v_f = a*t + v_i`
where:
- vf = final velocity
- a = constant acceleration
- t = time duration of constant acceleration
- vi = initial velocity
This would give you the velocity of the object after the same amount of time.
Motion Calculators:
- Duration (Time) of Free Fall
- Distance (Height) of Free Fall
- Final Velocity of a Free Fall
- Time from the distance and velocity.
- Travel Duration at Constant Acceleration
- Velocity from the distance and time.
- Distance from the velocity and time.
- Distance from initial displacement, velocity and time
- Distance from initial displacement, velocity, time and constant acceleration
 Free Fall Calculators
Free Fall Calculators
- Free Fall (time): Computes the duration of time that an object will be in free fall based on the height and the acceleration due to gravity.
- Free Fall (distance): Computes the distance that an object will be in free fall based on the duration of the fall and the acceleration due to gravity.
- Free Fall (Velocity at Impact): Computes the final velocity of an object after a free fall based on the height and the acceleration due to gravity.
- Free Fall (Energy on Impact): Computes the kinetic energy at impact based on the height of free fall, acceleration due to gravity and the mass of the object.
- Model Rocket Altitude: Computes the estimated maximum altitude of a rocket based the distance from the launch point and the angle to top point of flight (zenith).
- Object Height by Time to Drop: Estimates the height of an object based on the time it takes for an object to drop from the top of it.
- Elevation of Object (angles and separation): Computes the height of an object based on two angle measurements and the distance between them.
- Distance Traveled at Constant Acceleration: Computes the distance traveled by an object after a period of time, based on its initial distance from the origin, initial velocity and a constant acceleration.
- g (acceleration due to gravity at sea level): Acceleration due to Gravity (g) at sea level on Earth is 9.80665 m/s2.
Notes
See this video discussing a real use for this equation:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?feature=player_embedded&v=z68vta3N5kg
