vx=w⋅√g2h
(h)Height of fall | ||
(w)Horizontal distance traveled | ||
(g)Acceleration due to gravity | ||
Tags | |
UUID | e45c8c4c-df34-11e5-9770-bc764e2038f2 |
The velocity equation, vx= w⋅√g/2h, computes the horizontal velocity (vx) needed to span a horizontal distance (w) in the time it takes to fall from a height (h) under the acceleration due to gravity (g).
INSTRUCTIONS: Choose your preferred units and enter the following:
- (w) Horizontal distance
- (h) Height of fall
- (g) Acceleration due to gravity
The calculator computes the velocity (vx) in meters per second. However, this can be automatically converted to other velocity units via the pull-down menu.
Example: The Brave Train Engineer
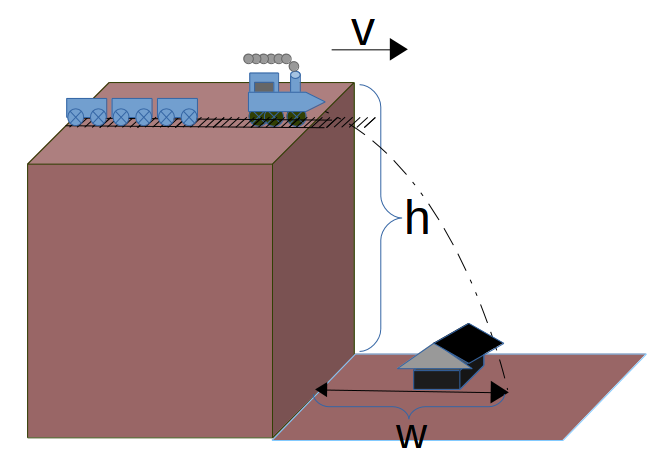 Fall Parameters
Fall Parameters
The Engineer of the train sees that the bridge is out, and even though he's decoupled the coaches from the engine, he knows he can't stop the engine in time. He also knows that there's a school at the bottom of the valley. The time to drop(Δt) is already set by the height (h) and the downward acceleration due to gravity(g). What horizontal speed (Vx) does the train need to achieve in order to clear the school before he hits the bottom, if the school is:
- (w) twenty five meters from the base of the cliff and
- (h) the cliff is 90 meters high.
Of course, he's on Earth and the downward acceleration due to gravity (g) can be approximated at 9.8 m/s2,
Reference
- Light and Matter(Dr. Benjamin Crowell) Chapter 6.2 Coordinates and components
Collections
- Comments
- Attachments
- Stats
No comments |
