The Rebar and Concrete in a Slab calculator computes the total length and weight of rebar and the volume and weight of concrete needed for a slab. This takes into account the concrete displaced by the rebar.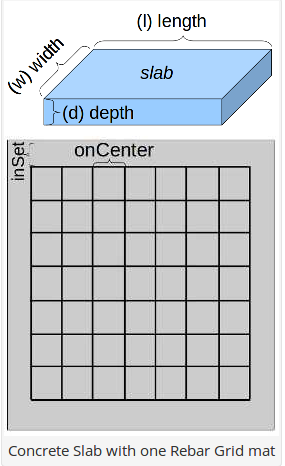
INSTRUCTIONS: Choose units and enter the following:
- (L) Length of the slab
- (W) Width of the slab
- (D) Depth of slab
- (rS) Rebar Size (2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,14,16,18,20)
- Use Size "0" for No Rebar
- (oC) On-center spacing Rebar
- (i) Inset distance from edge of slab
- (M) Number of mats
- (LF) Lapping Factor. 40 (default) and 60 are common.
- (RL) Rebar Stick Length
- (RC) Rebar Stick Cost
Rebar and Concrete in a Slab: The calculator returns:
- Total Length of rebar in feet and the number of sticks.
- Total Weight of rebar in pounds.
- Estimated Rebar Cost in U.S. dollars
- Total Volume of concrete in cubic yards. Note: this accounts for the concrete displaced by rebar.
- Total Weight of Slab in pounds. Note: this includes the weight of rebar and concrete, and takes into consideration the concrete displaced by rebar.
However, the above can be automatically converted to compatible units via the pulldown menu.
The Math / Science
.png)
The rebar algorithm calculates the length of rebar in the grid based on the slab dimensions, spacing, inset, number of mats, rebar size and lapping factor. Based on the rebar length and size, the weight of rebar is computed. Based on the slab dimensions and the volume displaced by rebar, the volume of concrete is computed.
Rebar Usage
Reinforcement bars are often used in concrete including common slabs. This formula provides a length and weigh calculation that is useful in understanding the additional load of the slab added by the rebar steel. It is also useful for calculating the weight of rebar when considering transport. Steel is dense and heavy. Most vehicles would be considerably overloaded in weight of rebar long before their potential volume is full, which poses a significant safety issue. In the U.S., most pickup trucks are rated at a half or three quarters ton load rating. This rating indicates the safe weight of a load that can be carried. The rebar weight formula can help determine how many trips are required to transport the load of reinforcement steel safely.
This is useful for:
- The determination of bar length in concrete slab
- The weight of rebar in concrete slab
Lapping Length
When the dimensions of your slab or wall exceed the length of a single piece of rebar, it is required to lap bars and tie them to create the added length. There are a few considerations. First, the length of the lap is often specified as 40 times the diameter of the rebar. In this case, 40 is lapping factor. 60 is also a common factor, but the engineering specifications should always be applied. See these YouTube videos to better understand rebar lap:
Second, the typical length of pre-cut rebar is 20', 40' and 60' in the United States.
Reinforcement Bar (rebar) Functions
- Length of Rebar in Grid: Computes the total length of rebar needed for one or more mats of rebar in a concrete slab based on slab dimensions, rebar spacing, inset from slab edge, number of mats, length of pre-cut rebar sticks, and a rebar lapping factor.
- Weight of Rebar in Grid: Computes the total length and associated weight of rebar needed for one or more mats of rebar in a concrete slab based on slab dimensions, rebar spacing, inset from slab edge, number of mats, length of pre-cut rebar sticks, a rebar lapping factor and the size of rebar.
- Rebar and Concrete in Slab: Computes the total length and weight of rebar and the volume of concrete needed for a slab. The weight and volume calculations take into account the concrete displaced by the rebar. Also provides the total weight of the slab and the cost of rebar.
- Wall (Rebar Concrete and Forms): Computes the length and weight of reinforcement bars (rebar), volume of concrete and the surface area of forms for a wall based on the dimensions of the wall.
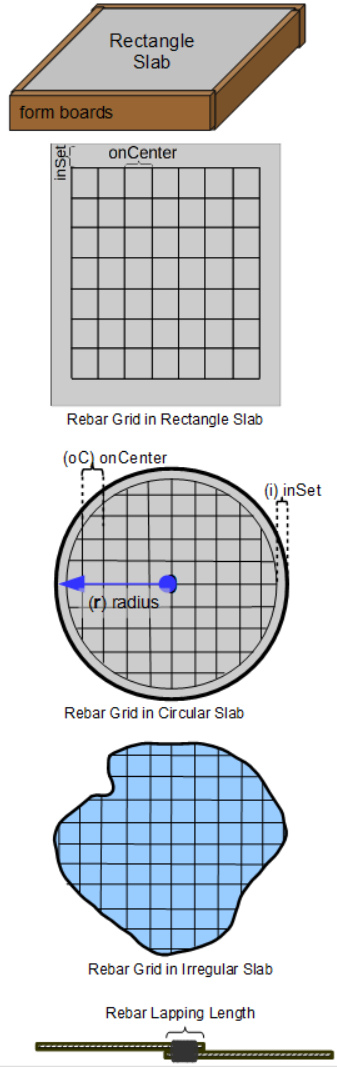
- Rebar in an Irregular Shaped Slab: Estimates the total length and weight of reinforcement bars (rebar) needed for an irregular shaped concrete slab.
- NEW Rebar Around Irregular Shaped Area: Estimates the total length and weight of rebar and concrete needed for a slab with an irregular shaped void (e.g. swimming pool) inside the slab.
- Rebar in a Circular Slab: Estimates the total length and weight of reinforcement bars (rebar) needed for a circular shaped concrete slab.
- Rebar Lapping Length: Computes the length overlap needed at rebar joints based on rebar size and a lapping factor.
- Rebar Cost Estimate: Computes the total cost of rebar based on the length being purchased, length of the individual pieces being bought and unit price of one piece of rebar.
- Weight of Rebar: Computes the total weight of rebar based on the length and size of rebar.
- Concrete Displaced by Rebar: Estimates the net weight added to a slab by adding rebar, and the reduction in concrete cause by adding rebar.
- Weight of Slab with Rebar: Estimates the weight of a rectangular slab with rebar base on the slab dimensions, rebar size and space and the know density of both concrete and rebar (steel). It also includes the individual weight of the components and the volume of concrete accounting for that displaced by rebar.
- Rebar Price per Pound: Computes the price per pound of rebar based on the unit cost of a rebar stick, its length and size (2-20).
- NEW Chairs for Rebar Grid: Computes the number of chairs needed to suspend a rebar grid.
- NEW Rebar and Concrete in Slab by Area: Estimates the total length and weight of rebar and the volume and weight of concrete needed for a slab by the surface area, depth and rebar specs (size, spacing, inset, mats, etc.).
See also the Calculadora de Barras de Refuerzo Collection for the Spanish version of the above.
Pole Barn Calculator
The Pole Barn Calculator contains functions to compute the construction materials for a pole barn with concrete piers, a slab, wood framing, roof trusses for a normal gabled roof and metal panels and trim for the roof and siding.
- Gable Roof Metal: This estimates the materials needed for a metal roof for a simple gabled roof based on the roof dimensions.
- Purlins for a Roof: This computes the total number and length of purlins for a simple gable roof based on the ridge length of the roof, the roof pitch and the span of the roof.
- Trusses Needed for Roof: This computes the number of trusses needed for a roof based on the ridge length and spacing.
- Metal Siding for Gable Ends: This computes the metal siding materials (vertical panels) for a wall under a gable roof end based on the dimensions.
- Metal Siding for Gable End with Door: This computes the metal siding materials for a wall under a gable roof end based on the dimensions.
- Girts for a Building: This computes the number of rows of girts and their lengths for a building.
- Wall Beams for a Building: This computes the lengths beams for the outer wall of a building.
- Posts for a Building: This computes the number of vertical posts for a building based on dimensions and spacing.
- Rebar and Concrete in a Slab: This computes the total length and weight of rebar and the volume of concrete needed for a slab.
- Piers for a Building: This computes the number of piers for a building and the amount of concrete needed.
- Pole Barn Materials: This computes the top to bottom framing and roofing materials needed for a pole barn (see picture) based on a few dimension.
- Pole Barn Metal Roof and Siding Cost: This uses an estimated the linear feet of metal panels needed for a pole barn with a door way, and provides an estimated cost for the metal panels for the roof and siding based on a the dimension and cost per linear foot of panels.
- Corrugated Metal Paint or Coating Volume: This estimates the volume of paint or other coating (e.g., spray insulation) is needed for a corrugated surface.
IMPORTANT NOTE: Confirm all calculations with authoritative sources such as architectural drawings before risking health or wealth on the results of any calculator, and ALWAYS adhere to government approved building codes.
Masonry Calc (Concrete, Brick and Block, Rebar)
The MASONRY suite includes collections of functions associated with product estimations on projects done with brick, block, concrete and rebar.
Concrete Slab Calculators
The following functions apply to estimating the amount of concrete, rebar, form boards and water needed for concrete slabs of different shapes: rectangular with squared corners, circular including semi-circle, and polygon shapes from triangular up (e.g., pentagon for 5 sides and dodecagon for 12 sided polygon).
Rectangle Slab
- Rebar and Concrete in a Slab: Computes the total length and weight of rebar and the volume and weight of concrete needed for a rectangular slab, taking into account the concrete displaced by the rebar.
- Concrete in Rectangle Slab: Computes the volume of concrete in a rectangle (squared corners) slab based on the dimensions. It includes the volume of concrete in cubic yards and the equivalent volume in bags of concrete. It also includes the surface area, length of form boards, and the water requirement.
- Slab Weight: Computes the weight, volume of concrete and surface area of a rectangle slab based on the length, width and depth of the concrete of the slab and the density of concrete.
- Weight of Slab with Rebar: Computes the weight of a rectangle slab with rebar based on the length, width and depth of the concrete of the slab, the density of concrete and the size and spacing of rebar. It includes total weight (concrete and rebar), and the contribution of weight from rebar and concrete separately.
- Slab Area and Perimeter: Compute the surface area and perimeter of a rectangular slab based on the dimensions.
Circular Slab
- Volume of Circular Slab: Computes the slab surface area, perimeter and cubic yards of concrete in a circular slab based on the diameter and depth. It also provides, the equivalent volume in 80lb, 60lb and 40lb bags of concrete and the water requirement.
- Circular Slab Weight: This computes the weight of the concrete in a circular slab based on the diameter, depth and density of concrete.
- Rebar and Concrete in a Circular Slab: This computes the length and weight of rebar in a rectangular slab. It also computes the total weight of the slab including concrete, taking into account the concrete displaced by rebar.
- Semi-Circle Slab Volume: Computes the volume of concrete needed for a semi-circular slab based on the radius and depth.
- Semi-Circle Slab Weight: Computes the weight of concrete in a semi-circular slab based on the radius, depth and density of concrete.
Polygon Slab
- Concrete in Polygon Slab: Computes the surface area and cubic yards of concrete for a polygon slab based on the dimensions and depth. It also provides the equivalent volume of concrete in 80lb, 60lb and 40lb bags of concrete.
General Functions
- Concrete Weight: Computes the weight of a specified volume (e.g., 2.3 cubic yards) of concrete.
- Price of Delivered Concrete: Computes the price of delivered concrete based on the volume, price per cubic yard, pumping cost, delivery distance, and mileage.
- Water Needed for Concrete: Compute the amount of water needed to make a volume of concrete.
- Concrete Displaced by Rebar: Computes the volume of concrete displaced by a length of rebar based on the length and size of rebar.
Masonry Walls (Brick, Block, Mortar Joints)
- Brick or Block Wall: Computes the number of brick or block needed for a wall based on dimensions.
- Bricks or Blocks in a Wall
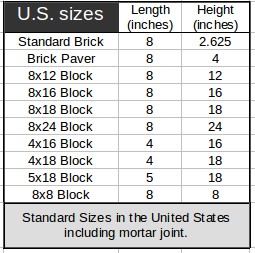 : Computes the number of standard U.S. brick or block needed for a wall using feet and inches.
: Computes the number of standard U.S. brick or block needed for a wall using feet and inches. - European Brick or Block in a Wall
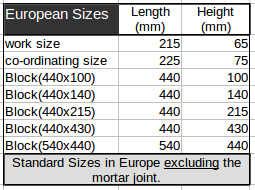 : Computes the number of standard European bricks or block in a wall using meters and centimeters.
: Computes the number of standard European bricks or block in a wall using meters and centimeters. - Custom Stone in a Wall: Computes the number of masonry units (stone, block or stone) in a wall based on the dimensions of the wall and the dimensions of the units and the thickness of the mortar joints. It also returns the number of rows needed and the number of stone per row.
- Concrete, Rebar and Forms for Wall: Computes the volume of concrete, amount of rebar and the surface area of forms for a concrete wall.
Foundations - Footers - Piers
- Blocks in a Foundation: Computes the number of blocks needed for a foundation based on the dimensions of the foundation and the size of the blocks with a standard size mortar joint.
- Concrete in a Poured Foundation
: Compute the volume of concrete, the square feet of the forms and the number of 4'x8's needed for the forms.
- Concrete in a Footer: Computes the volume of concrete for a footer based on the length, width and depth of the footer.
- Concrete in a Footer (Cross Section): Computes the volume of concrete for a footer based on the length and cross-section area of a footer
- Concrete in a Pier: Computes the volume of concrete in a circular pier based on the radius and depth of the pier.
- Piers for a Building: Computes the number of piers and volume of concrete need for the piers of a building (e.g., pole barn) base on the building dimensions, pier spacing, diameter and depth.
- Concrete around Circular Post: Computes the volume of concrete around a number of round posts in a round hole based on the size of the hole and dimensions of the post.
- Concrete around Square Post:
Computes the volume of concrete around a number of square post (e.g., 6x6) in round hole based on the dimensions of the post, depth and width of the round hole.
