Distance - constant velocity
vCalc Reviewed
`dx = x_0 + v_0 * "t" `
Tags | |
UUID | 63cf8d3c-0d14-11e4-b7aa-bc764e2038f2 |
The Distance - Constant Velocity calculator uses the equation, dx= x0+v0⋅t, to compute the total linear displacement (distance travelled).
INSTRUCTIONS: Choose the preferred units and enter the following;
- (x0) This is the initial displacement.
- (v0) This is the initial velocity.
- (t) This is the duration of the motion or travel.
Distance: The calculator returns the distance in meters. However, this can be automatically converted to other length or distance units via the pull-down menu.
The Math / Science
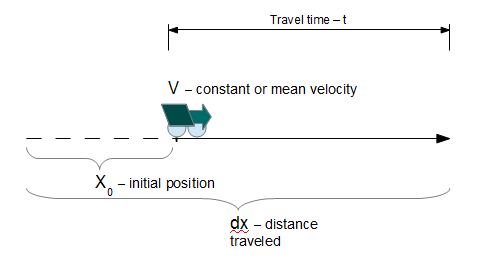 Motion under Constant Velocity
Motion under Constant Velocity
This calculator computes the distance an object travels as a function of time traveling at a constant initial velocity with the addition of an initial displacement (distance). This equation ignores external forces and so the object continues its motion at its initial constant velocity, `v_0`, as an expression of Newton's First Law.
where:
- `v_0` - Initial velocity at time t = 0
- `x_0` - initial displacement at time t = 0
- t - time of travel in the x-direction
Motion Calculators:
- Compute Duration (Time) of Free Fall
- Compute Distance (Height) of Free Fall
- Compute Final Velocity of a Free Fall
- Compute the time from the distance and velocity.
- Compute the velocity from the distance and time.
- Compute the distance from the velocity and time.
- Distance from initial displacement, velocity and time
- Distance from initial displacement, velocity, time and constant acceleration
Reference
- Young, Hugh D., Roger A. Freedman, A. Lewis Ford, and Francis Weston Sears. "2.4." Sears and Zemansky's University Physics: With Modern Physics. San Francisco: Pearson Addison Wesley, 2004. 51. Print.
This equation, Distance - constant velocity, is used in 3 pages
Calculators
- Comments
- Attachments
- Stats
No comments |
This site uses cookies to give you the best, most relevant experience. By continuing to browse the site you are agreeing to our use of cookies.

