Zero-order rate law (Integral form)
Tags | |
UUID | b927507c-2075-11e6-9770-bc764e2038f2 |
The Zero-order Rate Law (integral form) calculator computes the amount of reactant (concentration) at a certain point of time during a reaction.
INSTRUCTIONS: Choose units and enter the following:
- [A0] Initial Concentration of Substance A
- (k) reaction rate constant (units: mol/L*sec)
- (t) Duration of Reaction
Amount of Reactant [A]: The calculator returns the concentration of reactant in moles per liter (mol/L).
Chemistry Rate Law Calculators
- Zero Order Rate Law (Integral form)
- Zero Order Half Life
- Zero Order Rate Law
- First Order Rate Law (Integral form)
- First Order Half Life
- First Order Rate Law
- Second Order Rate Law (Integral form)
- Second Order Half Life
- Second Order Rate Law
The Math / Science
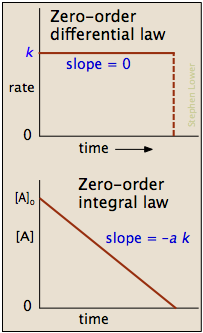 The zero-order rate law (integral form)[1] equation calculates the amount of reactant at a certain point of time during the reaction. Remember that rate is a differential equation in mathematics and physics that can be integrated, a full integration of the differential form of zero-order can be found here. The zero-order rate law (integral form) equation is:
The zero-order rate law (integral form)[1] equation calculates the amount of reactant at a certain point of time during the reaction. Remember that rate is a differential equation in mathematics and physics that can be integrated, a full integration of the differential form of zero-order can be found here. The zero-order rate law (integral form) equation is:
[A] = [A0] - k⋅t[2]
where
- [A] = Amount of Reactant
- [A0] = initial concentration of substance A in units of (mol/L)
- k = rate constant in units of (mol/L*sec)
- t = duration of the reaction in units of (sec)
Related Topics
Supplement Material
- Khan Academy: Rate law and reaction order
References
[1]https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rate_equation
[2]Whitten, et al. 10th Edition. Pp. 626,629,631
[Picture]http://chemwiki.ucdavis.edu/Core/Physical_Chemistry/Kinetics/Reaction_Rates/Zero-Order_Reactions
Collections
- Comments
- Attachments
- Stats
No comments |

