Half-Life (second order)
Tags | |
UUID | cccb768b-1dd8-11e6-9770-bc764e2038f2 |
The Second order Half-Life calculator computes the half-life based on the temperature dependent reaction rate constant and the concentration of the substance.
INSTRUCTION: Choose units and enter the following:
- (k) Temperature dependent reaction rate constant
- [A0] Initial Concentration of Substance.
Half-Life (t½): The calculator returns the half-life in seconds.
Chemistry Rate Law Calculators
- Zero Order Rate Law (Integral form)
- Zero Order Half Life
- Zero Order Rate Law
- First Order Rate Law (Integral form)
- First Order Half Life
- First Order Rate Law
- Second Order Rate Law (Integral form)
- Second Order Half Life
- Second Order Rate Law
The Math / Science
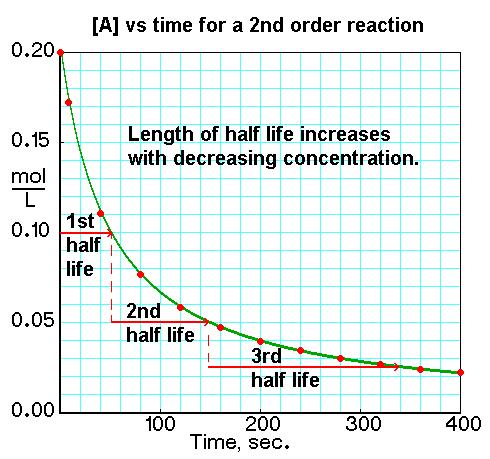
The half-life of a chemical reaction is defined as the time required for half the amount of a reactant to be converted into product. To find the half-lives of different order reactions, we use integrated rate laws and rate constants to relate concentration to time. There are three different rate laws that can be used to find the half-life of a chemical reaction: zero, first, and second order.
Second order reactions are dependent on concentration, just like first order reactions; however, second order reactions react much faster than first order. The rate for second order reactions is rate = k[A]2, so it decreases exponentially, unlike first order reactions. The rate law is 1/[A] = kt + 1/[A]0 and the equation used to find the half-life of a second order reaction is t1/2 = 1 / k[A]0.
Where
- k is the temperature-dependent reaction rate constant
- t1/2 is the half life
- [A]0 is the initial concentration
References
Whitten, et al. "Chemistry" 10th Edition. Pp. 629
See Also
Calculators
Collections
- Comments
- Attachments
- Stats
No comments |