The Piston Crevice Volume calculator computes the crevice volume (Volc) of a 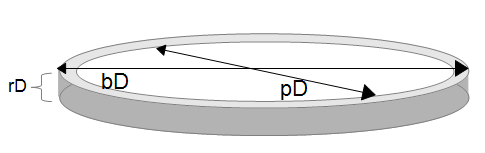 Piston Ring Crevice combustion engine cylinder as a function the bore diameter(bD), piston diameter (pD) and the top ring depth (rD).
Piston Ring Crevice combustion engine cylinder as a function the bore diameter(bD), piston diameter (pD) and the top ring depth (rD).
INSTRUCTIONS: Choose your preferred units, the default is inches and mils, and enter the following:
- (bD) Bore Diameter
- (pD) Piston Diameter
- (rD) Top ring depth
| Inch Equivalences | |||
| Fraction | Decimal | Mils | |
| 1/16th | 0.0625 | 62.5 | |
| 1/32th | 0.03125 | 31.25 | |
| 1/64th | 0.015625 | 15.625 | |
Cylinder Crevice Volume: The volume is computed in cubic inches. However, the can be automatically converted to other volume units (e.g. cubic centimeters aka CCs) via the pull-down menu.
The Math
Engine Math (Baechtel) and I disagree on this equation. Engine Math takes the difference of the diameters (bore and piston), multiplies that difference by the circumference of the bore to create the surface area of the crevice and then multiplies that surface area by the depth to the top ring to get the volume. The surface area of that equation is geometrically wrong. Fortunately these crevice volumes don't affect much. But the mathematician in me can't let it sit. The correct formula for the crevice surface area is the difference between the two circle areas defined by the bore diameter and the piston diameter, using PI*r2 where r is half of the respective diameters. THEN multiply the correct surface area by the crevice depth from the deck to the top piston ring. I'm sure Baechtel's answer is probably good enough, but this is more correct.
Combustion Engine Calculators
Ratios and Lengths
- Cylinder Bore Diameter: Computes the diameter (bore) based on the engine displacement, number of cylinders and the stroke length.
- Bore Stroke Ratio
: Computes ratio based on the diameter of the bore and the length of the stroke.
- Combustion Ratio: Computes ratio base on the minimum and maximum displacements of the cylinder at the beginning (1-Induction) and compressed (3-Power) portions of the combustion cycle
- Displacement Ratio: Computes ratio based on the volumes at the beginning and end of the stroke.
- Rod and Stroke Length Ratio: Computes ratio base on the rod and stroke lengths.
- Stroke Length: Computes the required stroke length based on the total engine displacement, number of cylinders and the bore.
- Piston Position: Computes the piston position based on the crank angle, crank radius, and rod length.
- Piston Deck Height: Computes deck height based on Block Height, Rod Length, Stroke Length, and Pin Height.
Volumes and Displacements
- Total Volume (displacement) of a Combustion Engine: Computes volume based on the bore, stroke and number of cylinders.
- Volume (displacement) of a Engine Cylinder: Computes volume based on the bore and stroke.
- Volume (displacement) of an Engine with an Overbore: Computes volume based on the stroke, bore, overbore and number of cylinders.
- Equivalent Volume of a Rotary Engine: Estimates rotary engine volume based on the swept volume and number of pistons.
- Carburetor Air Flow: Estimates the volumetric flow of air through a carburetor based on a four-stroke engine's displacement, RPMs, and volumetric efficiency.
- Compressed Volume of a Cylinder:
Compute volume when the piston is at the end of the stroke and the chamber is at its smallest (and most compressed) volume, based on the chamber, deck, crevice, chamfer, gasket, valve relief and dome/dish volumes. This is the second volume (V2) in the Compression Ratio calculation.
- Volume of a Gasket: Computes gasket volume (displacement) based on the inner and outer diameters and the gasket's thickness.
- Volume of a Cylinder Deck: Computes the deck volume based on the deck height and the bore.
- Volume of a Cylinder Crevice: Computes crevice volume based on the piston diameter, cylinder bore and the crevice height.
- Volume of a Cylinder Chamfer: Computes chamfer volume based on the cylinder diameter and the chamfer height and width.
- Clearance Volume of a Piston: Computes the volume remaining in the combustion chamber when the piston is at its top dead center (TDC) which is the space above the piston crown when it's at its highest point in the cylinder.
- Engine Compression Ratio: Computes the ratio of the volume of the combustion chamber with the piston at its bottom dead center (BDC) to the volume with the piston at its top dead center (TDC).
Speeds and RPMs
- Piston Speed (mean): Computes the mean (average) piston speed based on stroke length and RPMs.
- Max Piston Speed: Computes max speed based on stroke length and RPMs
- RPMs: Computes revolutions per minute based on piston speed and stroke length.
Other Automotive Calculators
- Camber Angle
- Camber Offset
- Breakover angle - Ground clearance between axles
- Approach angle - Ground clearance in front of or behind vehicle.
- Belt Length
- Belt Speed.
- Pulley RPMs
- 2nd Pulley RPMs
- 2nd Pulley Diameter
- RPM of 4th pulley on three shafts
- 2nd Gear RPM
