Processing...
`W _"(lift mass)" = "F" * "y" "/" "x" `
Enter a value for all fields
The Weight Lifted by Leverage calculator (`W = F * y/x`) 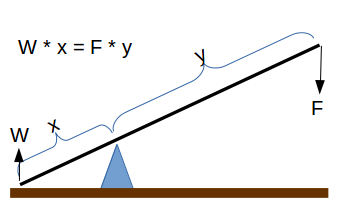 computes the mass (W) that can be lifted by the use of a lever when the downward mass / weight and the two lengths (x and y) on either side of the fulcrum are known.
computes the mass (W) that can be lifted by the use of a lever when the downward mass / weight and the two lengths (x and y) on either side of the fulcrum are known.
INSTRUCTIONS: Choose units and enter the following:
- (F) Downward Force (weight) opposite the fulcrum from the object.
- (y) Length of Beam on opposite side of fulcrum from the object (see diagram).
- (x) Length of Beam on object's side of fulcrum (see diagram)
Weight Lifted by Lever (W): The calculator computes the mass/weight (W) in kilograms. However this can be automatically converted to other mass or weight units via the pull-down menu.
The Math/Science
A lever is a simple machine where the ratio of the product of the lengths and forces on opposite sides of a fulcrum are equal.
Mechanical Leverage Functions
- (y) Beam Length: computes the required length of a beam above the fulcrum for a lever to raise a weight (W) based on the downward weight applied (F) and the length below the fulcrum (x).
- (W) Lift Weight: computes the weight that can be lifted with a lever based on the length of the beam (y) above the fulcrum, the length (x) below the fulcrum and downward weight applied (F).

- (x) Fulcrum Position: computes the length from the object to the fulcrum needed in a lever to lift a weight (W) with a downward force (F) with a beam of length (L), where L = x + y (see below).
- (F) Downward Force or Weight: computes the mass needed to create the downward force (F) to raise the object with a lever.
- L = x+y : computes the sum of two lengths
Simple Machine Calculators
- Lever Beam Length: Computes the length of a lever (beam) on one side of a fulcrum needed to lift an object based on the objects weight and the length of the beam on the other side of the fulcrum.
- Leverage Lift Weight: Computes the weight that can be lifted using a lever based on the downward force and the length of the lever on either side of the fulcrum.
- Fulcrum Position (x): Computes the position of the fulcrum needed in a lever to lift a weight (W) with a downward force (F) with a beam of length (L), where L = x + y.
- Belt Length: Computes the length of a belt that goes around two pulleys of different diameters separated by a specific distance.
- Belt Speed: Computes the speed a belt travels based on the diameter of the pulley and the RPMs.
- Pulley RPMs: Computes the RPMs of a pulley based on the speed of the belt and the diameter of the pulley.
- 2nd Pulley RPMs: Computes the RPMs of a second pulley in a two pulley system when the RPM and Diameter are known for one pulley and the diameter of the second pulley is also known.
- 2nd Pulley Diameter:- Computes the diameter of a second pulley in a two pulley system based on diameter and RPM of one pulley and the RPMs of the second.
- Pulley System Tension: Computes the tension on a cable around a cable based on two weights.
- Pulley System Acceleration: Computes the belt or cable acceleration in a two mass pulley system.
- RPM of 4th pulley on three shafts: Computes the RPMs of a fourth pulley on
a three shaft system when the RMPs of the first shaft is known and the four diameters.
- 2nd Gear RPM: Computes the RPMs of a second gear when the RPM and number of teeth are known for the first gear, and the number of teeth are known for the second gear.
- Pulley RPMs: Computes pulley RPMs from belt speed and pulley diameter.
- Sum of Two Lengths: Computes the sum of two lengths (useful with lever calculations).
- Second Gear Torque: Calculates the torque of a second gear when the torque and number of teeth are known for the first gear and the number of teeth of the second gear is known.
- Leadscrew Torque (lift): Computes the torque required to lift a load with a square thread power screw assembly.