Processing...
`x = "L" / ( "W" / "F" +1)`
Enter a value for all fields
The Fulcrum Position calculator computes the distance (x) from the object to the fulcrum based on the length of the beam (L), the mass of the object (W) and the downward force (F).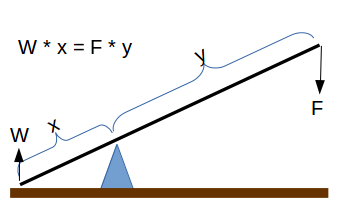
INSTRUCTIONS: Choose your preferred units and enter the following:
- (F) Downward force (weight) opposite the fulcrum from the object.
- (W) Mass (weight) of the object being lifted.
- (L) Total length of the beam (L = x+y in diagram)
Fulcrum Position (x): The calculator returns the length in meters. However this can be automatically converted to other length units via the pull-down menu.
The Math/Science
A lever is a simple machine where the ratio of the product of the lengths and forces on opposite sides of a fulcrum are equal as is represented in the following equation:
where:
- W = Weight or Mass lifted
- x = length of lever on the weight side of the fulcrum
- F = downward force
- y = length of lever on the downward force side of the fulcrum
Mechanical Leverage Functions
- (y) Beam Length: computes the required length of a beam above the fulcrum for a lever to raise a weight (W) based on the downward weight applied (F) and the length below the fulcrum (x).
- (W) Lift Weight: computes the weight that can be lifted with a lever based on the length of the beam (y) above the fulcrum, the length (x) below the fulcrum and downward weight applied (F).

- (x) Fulcrum Position: computes the length from the object to the fulcrum needed in a lever to lift a weight (W) with a downward force (F) with a beam of length (L), where L = x + y (see below).
- (F) Downward Force or Weight: computes the mass needed to create the downward force (F) to raise the object with a lever.
- L = x+y : computes the sum of two lengths
Simple Machine Calculators
- Lever Beam Length: Computes the length of a lever (beam) on one side of a fulcrum needed to lift an object based on the objects weight and the length of the beam on the other side of the fulcrum.
- Leverage Lift Weight: Computes the weight that can be lifted using a lever based on the downward force and the length of the lever on either side of the fulcrum.
- Fulcrum Position (x): Computes the position of the fulcrum needed in a lever to lift a weight (W) with a downward force (F) with a beam of length (L), where L = x + y.
- Belt Length: Computes the length of a belt that goes around two pulleys of different diameters separated by a specific distance.
- Belt Speed: Computes the speed a belt travels based on the diameter of the pulley and the RPMs.
- Pulley RPMs: Computes the RPMs of a pulley based on the speed of the belt and the diameter of the pulley.
- 2nd Pulley RPMs: Computes the RPMs of a second pulley in a two pulley system when the RPM and Diameter are known for one pulley and the diameter of the second pulley is also known.
- 2nd Pulley Diameter:- Computes the diameter of a second pulley in a two pulley system based on diameter and RPM of one pulley and the RPMs of the second.
- Pulley System Tension: Computes the tension on a cable around a cable based on two weights.
- Pulley System Acceleration: Computes the belt or cable acceleration in a two mass pulley system.
- RPM of 4th pulley on three shafts: Computes the RPMs of a fourth pulley on
a three shaft system when the RMPs of the first shaft is known and the four diameters.
- 2nd Gear RPM: Computes the RPMs of a second gear when the RPM and number of teeth are known for the first gear, and the number of teeth are known for the second gear.
- Pulley RPMs: Computes pulley RPMs from belt speed and pulley diameter.
- Sum of Two Lengths: Computes the sum of two lengths (useful with lever calculations).
- Second Gear Torque: Calculates the torque of a second gear when the torque and number of teeth are known for the first gear and the number of teeth of the second gear is known.
- Leadscrew Torque (lift): Computes the torque required to lift a load with a square thread power screw assembly.