Processing...
`psi_g = sin^(-1) (h/R)`
Enter a value for all fields
The Grazing Angle calculator computes the angle above the horizon to a radar antenna.
INSTRUCTIONS: Choose units and enter the following:
- (R) This is the range to the radar.
- (h) This is the height of the radar.
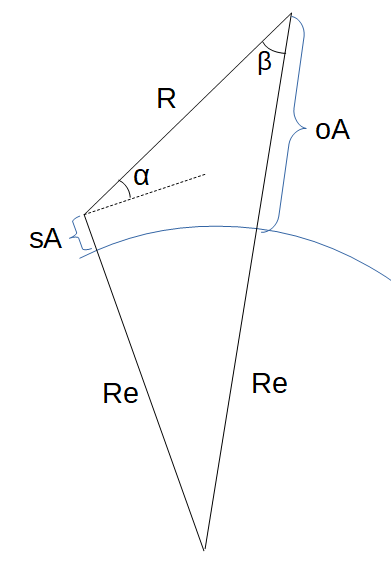
Grazing Angle (ψ):" The calculator return the grazing angle in degrees. However this can be automatically converted to other angle units via the pull-down menu. To compute the Grazing Angle considering the curvature of the Earth, CLICK HERE.
The Math / Science
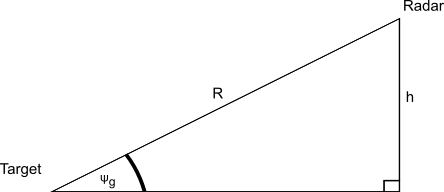 The formula for the grazing angle is:
The formula for the grazing angle is:
`ψ_g = sin^(-1) (h/R)`
where:
- ψg = grazing angle
- R = range to radar
- h = height of radar
The Grazing Angle equationSignal-to-Noise of a Synthetic Aperture Radar.
- SNR Gain Due to Azimuth Processing (coherent pulse integration)
- SNR Gain Due to Range Processing (pulse compression)
- Target Radar Cross Section
- Monostatic SAR Transmitter Antenna Gain Factor
- Radar Atmospheric Loss
- SAR Duty Factor
- Grazing Angle
- Slant Range
- Slant Range (Beta Angle)
3D Vector Calculator Functions
- k V - scalar multiplication
- V / |V| - Computes the Unit Vector
- |V| - Computes the magnitude of a vector
- U + V - Vector addition
- U - V - Vector subtraction
- |U - V| - Distance between vector endpoints.
- |U + V| - Magnitude of vector sum.
- V • U - Computes the dot product of two vectors
- V x U - Computes the cross product of two vectors
- Vector Angle - Computes the angle between two vectors
- Vector Area - Computes the area between two vectors
- Vector Projection - Compute the vector projection of V onto U.
- Vector Rotation - Compute the result vector after rotating around an axis.
- (ρ, θ, φ) to (x,y,z) - Spherical to Cartesian coordinates
- (x,y,z) to (ρ, θ, φ) - Cartesian to Spherical coordinates
- (r, θ, z) to (x,y,z) - Cylindrical to Cartesian coordinates
- (x,y,z) to (r, θ, z) - Cartesian to Cylindrical coordinates
- ^ Performance Limits for Synthetic Aperture Radar - Second Edition. Sandia National Laboratories, Albuquerque, NM. Printed February 2006.