Processing...
`R = f(sA,alpha,oA)`
Enter a value for all fields
The Slant Range function computes the slant range from a ground station to an object (satellite or aircraft) based on the station and object altitudes and the elevation angle. 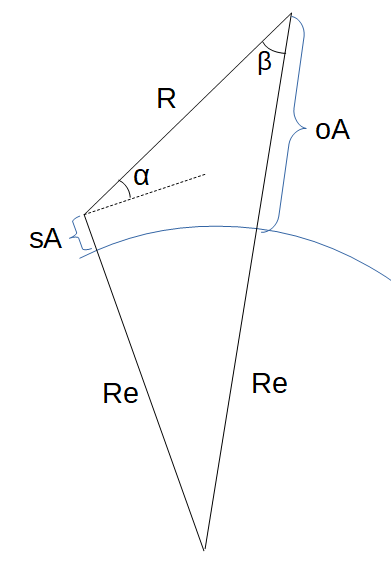
INSTRUCTIONS: Choose units and enter the following:
- (sA) Station Altitude above Mean Earth Radius
- (α) Elevation Angle from the Station above the horizon to object.
- (oA) Object Altitude above Mean Earth Radius
Slant Range (R): The range is returned in kilometers. However this can be automatically converted to compatible units via the pull-down menu.
The Math / Science
The formula for the slant range uses both the law of sines and the law of cosines.
In the obtuse triangle shown (right):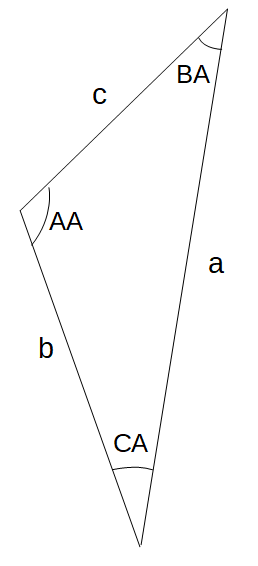
- Re = Mean Earth Radius
- b = Re + sA
- a = Re + oA
- c is the slant range
- CA is the Earth Central Angle
- BA is the subtended angle (β)
- AA = arcsine( a*sin(BA) / b )
- α = 90° - AA
` a/(sin("AA")) = b / (sin("BA")) = c / (sin("CA"))`
`c = sqrt( a^2 + b^2 - 2a*b*cos(CA) )`
Earth Model Calculators
- Slant Range using Position Vectors
- Slant Range from Elevation Angle (α)
- Slant Range using Subtended Angle (β)
- Distance to Horizon
- Angle of Satellite Visibility
- Grazing Angle
- XYZ to Latitude, Longitude, Altitude
- Earth WGS-84 Equatorial radius in meters: 6378137.0 m
- Earth WGS-84 Polar radius in meters: 6356752.31424518 m
- Earth Flattening Factor (WGS-84): 0.00335281066474748071984552861852
- Ellipse flattening factor: F = (Er - Pr)/Er
- Geocentric to Geodetic Latitude
- Geodetic to Geocentric Latitude
Oblate Spheroid Calculators and Data
- Earth WGS-84 Equatorial radius in meters: 6378137.0 m
- Earth WGS-84 Polar radius in meters: 6356752.31424518 m
- Earth Flattening Factor (WGS-84): 0.00335281066474748071984552861852
- Ellipse flattening factor: F = (Er - Pr)/Er
- Geocentric to Geodetic Latitude
- Geodetic to Geocentric Latitude
- Slant Range