The Snow Water Density (SWD) calculator computes the kilograms per meters cubed (kg/m3) for snow of different types or water at different temperatures per the US Geological Survey (USGS).
INSTRUCTIONS: Enter the following:
- (T) Choose a type of snow from the pull-down list.
- (Temp) Temperature for liquid water (default is 0º C)
DENSITY (ρ): The calculator returns the density in kilograms per cubic meters. However, this can be automatically converted to other density units via the pull-down menu.
Related Calculators:
- Compute the weight of snow on an area.
- Compute the weight of snow on a rectangular area.
- Compute the weight of snow on a polygon shaped area.
- Compute the weight of snow on a roof.
- Compute the amount of water in snow laying on land.
The Math / Science
Water density is a function of temperature. Snow Water Equivalent (SWE) is the product of snow depth and snow density. It can be presented in units of either kg/m2 or m:
SWE (`(kg)/(m^2)`) = snow depth (`m`) x snow density `((kg)/(m^3))`
SWE (`m`) = snow depth (`m`) x snow density `((kg)/(m^3))` / water density `((kg)/(m^3))`
You can calculate snow depth from SWE if you know the density of the snow. Of course, density of snow can range anywhere from 5% when ambient air temperature is 14 F, and can range up to 20% if the temperature is 32 F. The snow density will increase after the snowfall due to gravitational settling, packing, wind effects, melting and refreezing.
| Type of snow, ice or water | densities (kg/m³) |
| New snow (immediately after falling in calm) | 50-70 |
| Damp new snow | 100-200 |
| Settled snow | 200-300 |
| Depth hoar | 100-300 |
| Wind packed snow | 350-400 |
| Firn (granular snow) | 400-830 |
| Very wet snow and firn | 700-800 |
| Glacier ice | 830-917 |
| Snow Melt | 1002 |
| Water | f(Temp) |
| Sea Water | 1021.98 |
The equation will use a median value for the ranges in the density value column.
Water Related Calculators
- Underwater Pressure: Computes the added pressure exerted underwater by the water column directly overhead as a function of the density of the water, depth under water, and the acceleration due to gravity.
- Pore Water Pressure: Measure of the pressure of groundwater held within a soil or rock, in gaps between particles (pores), relative to atmospheric pressure.
- Osmotic Pressure: Computes the osmotic pressure based on the molar concentration of the solution (M), the temperature (T) and the Ideal Gas Constant (R).
- Density of water at STP: 998.2071 kg / m3
- Density of Deawater: 1,025 kg / m3
- Saltwater Intrusion: Uses the Ghyben-Herzberg Relation to compute the depth of fresh water in an aquifer below sea leve based on the depth of fresh water above sea level.
- Snow or Water Density: Returns the kilograms per meters cubed (kg/m3) for snow of different types or water at different temperatures per the US Geological Survey (USGS).
- Water Density by Temperature: Computes the density of water as a function of temperature, using the standard density of water (ρ) at standard temperature and pressure, and the unique temperature expansion coefficient of water.
- Pressure to Water Depth: Computes approximated depth of water where the pressure would occur.
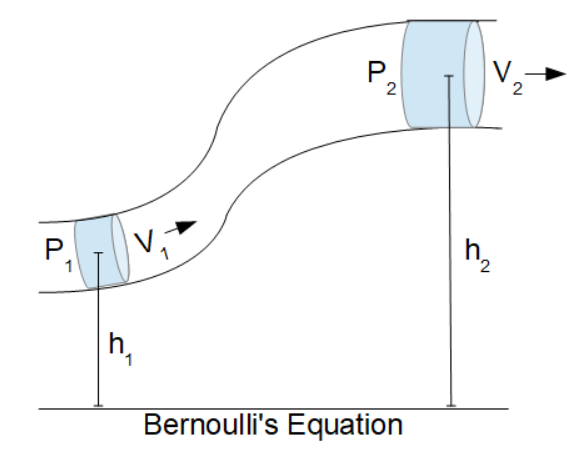
- Bernoulli's Equation (Pressure): Uses Bernoulli's equation to compute fluid pressure (p1) based on the fluid velocities, heights and second pressure (p2).
- Bernoulli's Equation (Velocity): Uses Bernoulli's equation to compute fluid velocity (v1) based on the pressures, heights and second velocity (v2).
- Bernoulli's Equation (Elevation): Uses Bernoulli's equation to compute elevation (h1) based on the pressures, fluid velocitities and second height (h2)
- Volume of Water in a Well: Compute the volume of water in a well based on the static water level and the diameter of the well pipe..
- Pressure to Water Depth: Computes the height needed to acheive a desired pressure considering the density of liquid (e.g., water).
- Pressure Head: Computes the pressure based on the height of Gravity-Fed water from a tank or resevoir.
- Underwater Pressure: Computes the added pressure exerted underwater by the water column directly overhead as a function of the density of the water, depth under water, and the acceleration due to gravity.
- Heat Load and Water Flow: Computes the ton of heat capacity associated with a volumetric flow of water and a change in temperature.
