The paired samples t-test calculator compares two different sample means from the same sample (Gravetter and Walllnau, 2013). In this case, all subjects participate in all conditions of the test variable.
INSTRUCTIONS: Enter the following:
- (tails) One-tail or Two-tail test.
- (α) Alpha Value (choose: 0.05, 0.01, 0.005, 0.001)
- (X,Y) Enter table of comma separated pairs for Group X and Group Y
Paired Samples t-test: The calculator returns the following:
- (n) Number of Pairs
- (X stats) The mean (M) and sample standard deviation (SD) of group X.
- (Y stats) The mean (M) and sample standard deviation (SD) of group Y.
- (DF) The degrees of freedom
- (CT) The critical t-value
- (t) The t-value
- (SE) The Standard Error value.
The Math/ Science
The computation for a paired samples t-test is similar to that of an independent samples t-test. Similar inputs are used, but it is important to remember they apply to the same sample, not two different samples. To demonstrate this, we will use the dataset "Comfortable TV viewing distance for college students" located HERE. The data presented here can be input to the equation, which will return the means and standard deviations of both test samples (M and SD) and a summary of the results, including degrees of freedom (df), a critical t-value, your t-score, and the standard error (SE).
If you plug in the data values, you should get a return string that looks like this: Sample 1: M = 6, SD = 1.67. Sample 2: M = 5.17, SD = 2.23. Summary: df = 5, critical t-value = 2.015, t-value = -0.62, and SE value is 1.35. This tells us that the difference between the two means is not significant, because our t-value is not beyond the critical t-value. In context, according to this hypothetical data, college students do not find one TV viewing distance (8ft or 12 ft) more comfortable than another; they are roughly equally comfortable.
References
Gravetter, F. J., & Wallnau, L. B. (2013). Statistics for the Behavioral Sciences. Wadsworth, CA: Cengage Learning.
The example provided in the dataset was adapted from the textbook.
Statistics Calculators
- Observational Stats: This function accepts a table (rows and columns separated by commas) of numbers and calculates observational statistics for any of the columns. This includes count, min, max, sum, sum of squares (Σx²), square of the sum (Σx)², mean, median, mode, range, mid point, rand, sort up, sort down, rand, population variance, population standard deviation, the sample/experimental variance, sample/experimental standard deviation.
- Simple Stats: This is also provides a full set of observational stats, but on a single row of numbers separated by commas. The observational stats include count, min, max, sum, sum of squares (Σx²), square of the sum (Σx)², mean, median, mode, range, mid point, rand, sort up, sort down, rand, population variance, population standard deviation, the sample/experimental variance, sample/experimental standard deviation.
- Frequency Distribution: This function lets you enter a string of numbers separated by commas, a low and high range and a number of bins. It then computes how many of the observations are in each of the bins between the high and low values designated.
- Paired Sample t-test: This computes the various parameters associated with the Paired Sample t-test.
- ANOVA (one way): The computes the F Score and details for one way analysis of variance for a nxm matrix of observations.
- (χ2) Chi-Square Test: This computes the Chi-Square value for an nxm array of data and provides the degrees of freedom.
- Linear Regression
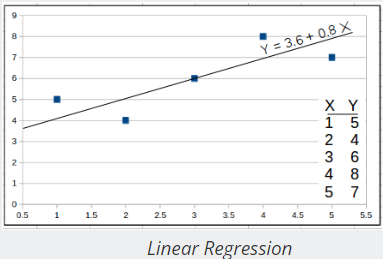 : This computes the regression line (least-squares) through a set of X and Y observations. It also computes the regression coefficient (r).
: This computes the regression line (least-squares) through a set of X and Y observations. It also computes the regression coefficient (r). - Least-squares Trend Inference : This is a linear equation used with Linear Regression to compute a predicted value of Y based on X.
- Wilcoxon Signed Rank Test: This provides the Wilcoxon statistics and critical value for two groups of numeric observations based on an alpha value and whether it's a one or two tailed test.
- Slope-Intercept form of a Line: This provides the slope intercept form (y = mx+b) of a line based on two coordinates.
- Slope between two points: This provides the slope between two coordinates.
- Linear Equation: This computes the range (y) of a linear equation (y = mx +b) and includes a graphing function.
- Probability between z SCORES:
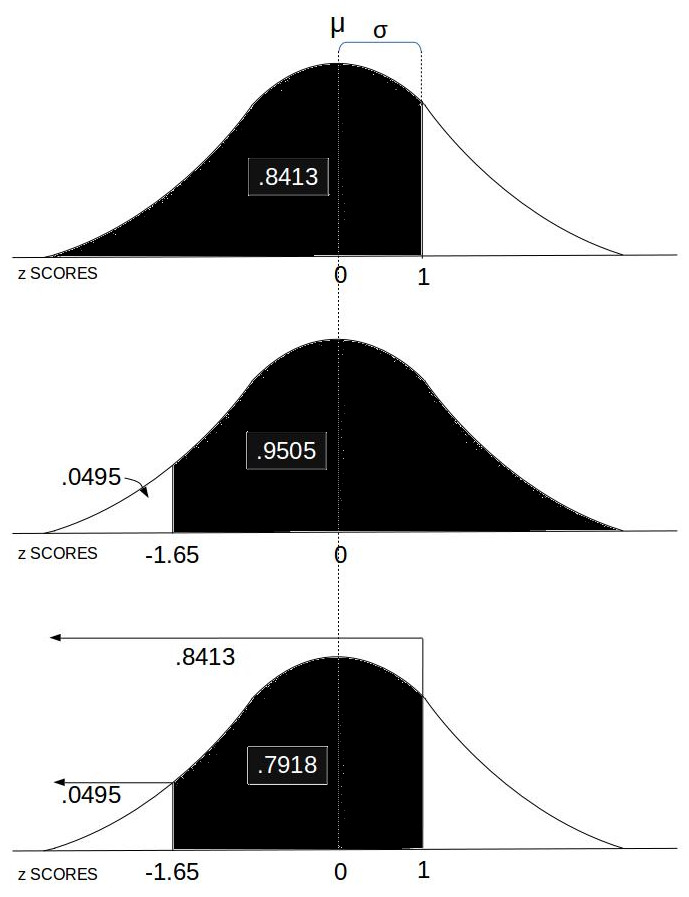 This computes the area under the Normal Distribution curve between two z SCOREs which equates to the probability of an event in that range.
This computes the area under the Normal Distribution curve between two z SCOREs which equates to the probability of an event in that range. - Stats Calc: College level statistics calculator with a bundle including most of the functions in this list.
- Count: This computes the number (n) of observations in a set of numbers.
- Minimum: This computes the minimum (min) value in a set of numbers.
- Maximum: This computes the maximum (max) value in a set of numbers.
- Numeric Sort: This sorts (ascending or descending) a set of comma separated numerical observations.
- Random Sample (k items): The provides a random subset of a specified size (k) in a set of comma separated numerical observations.
- Random Real Number in Range: The provides a random real number between two specified real numbers (upper and lower bounds).
- Radom Integer: The provides a random integer between two specified integers (upper and lower bounds).
- Frequency Distribution: This provides a frequency distribution table for a comma separated set of numbers with a specified number of frequency bins between a lower and upper data range.
- Sum (Σx): This is computes the sum of the values in a set.
- Sum of Squares (Σx²): This computes the sum of the squared values in a set.
- Sum Squared (Σx)²: This computes the square of the summed values in a set.
- Mean (μ): This computes is the mean (average) of values in a set.
- Median: This identifies the middle ordered value in a set of numbers.
- Statistical Mode: This identifies the most recurring observation in a set of numbers.
- Mid Point: This is identifies the mid point of the observation range in a set of numbers.
- Range: This is computes the difference between the max and the min values in a set of number.
- Population Variance (σ2): This computes the variance, a metric regarding the spread of values, for a population set of numeric values.
- Population Standard Deviation (σ): This computes the standard deviation for a population set of numeric values.
- Sample Variance (s2) : This computes the variance, a metric regarding the spread of values, for a sample set of numeric values within a greater population.
- Sample Standard Deviation (s): This computes the standard deviation for a sample set of numeric values within a greater population.
- z SCORE Formula: This computes the z SCORE for a value base on the mean and standard deviation.
- z SCORE: This computes the z SCORE for a value (Raw Score) based on a set of values, and whether that set is sample or population.
- Percentile: This computes the percentile of a value (y) in a set (X) of values.
- Standard Deviation of Mean (SDOM): This computes the standard deviation of mean, sometimes also known as the standard error of the mean (SEM), useful to helps quantify the uncertainty in the estimate of the mean.
- Percent Relative Standard Deviation (%RSD): This computes the percent relative standard deviation, also known as the coefficient of variation (CV). The %RSD is a measure of the dispersion of a probability distribution.
