Osmotic Pressure
Tags | |
UUID | a1be04e7-1c53-11e6-9770-bc764e2038f2 |
The Osmotic Pressure calculator computes the osmotic pressure based on the molar concentration of the solution (M), the temperature (T) and the Ideal Gas Constant (R).
INSTRUCTIONS: Choose units and enter the following:
- (M) molar concentration of the solution
- (T) temperature
Osmotic Pressure (Π): The pressure is returned in atmospheres. However, this can be automatically converted to compatible units via the pull-down menu.
The Math / Science
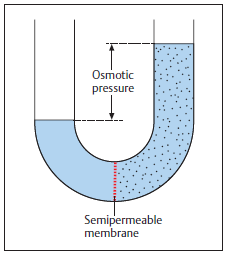
The Osmotic Pressure formula, Π = M•R•T, represents the pressure required to prevent a pure solvent from passing into a solution through osmosis, as shown in the figure below. Osmotic pressure plays an important role in cell regulation. It helps cells prevent too much water from either escaping or entering the cell, thus maintaining a homeostasis. Osmotic pressure can also be used to estimate molecular weights, particularly for higher weight molecules.
The Osmotic Pressure formula is:
Π = M•R•T
where:
- Π = Osmotic Pressure
- M = molar concentration of the solution
- R = ideal gas constant
- T = temperature
The default units are moles/liter for molar concentration and Kelvin for temperature.
Description
Osmotic pressure increases with temperature because temperature affects the number of solvent-membrane collisions per minute. It also increases with molarity because molarity leads to a higher or lower number of molecules hitting the membrane. A higher molarity leads to a stronger drive to equalize the concentration and increase disorder in the solution.
Supplemental Materials
Khan Academy - Diffusion and Osmosis

Water Related Calculators
- Underwater Pressure
- Pore Water Pressure
- Osmotic Pressure
- Density of water at STP
- Density of seawater
- Saltwater Intrusion
- Snow or Water Density
- Water Density by Temperature
- Compute the Depth of Water associated with a Pressure
- Bernoulli's Equation (Pressure)
- Bernoulli's Equation (Velocity)
- Bernoulli's Equation (Elevation)
- Volume of Water in a Well
References
Whitten, et al. "Chemistry" 10th Edition. Pp. 530
Wikipedia - Osmotic Pressure
Equations and Data Items
Collections
- Comments
- Attachments
- Stats
No comments |