The Pipe Coating Amount calculator computes the amount of coating material for the exterior surface area of a pipe based on the pipe diameter, length and the thickness of the coating. 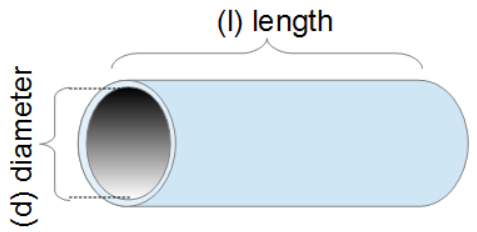
INSTRUCTIONS: Choose units and enter the following:
- (d) Diameter of Pipe (use exterior diameter)
- (l) Length of Pipe
- (t) Coating Thickness
- (n) Number of Pipes to Coat
Coating of Pipe (V): The calculator returns the volume of material to coat the surface area in gallons (or quarts) and liters (or milliliters). However, these can be automatically converted to compatible units via the pull-down menu.
The Math / Science
The equation for the amount of coating for a pipe is:
V =2π⋅(d/2)⋅l ⋅ t
where:
- V = Amount (volume) of Pipe Coating
- d = Diameter of Pipe
- l = Length of Pipe
- t = thickness of coating
Pipe Coating Guidelines
Pipes can be coated with various materials to protect them from corrosion and other environmental factors. Some common materials used for coating pipes include:
- Epoxy Coatings: Epoxy coatings are often used to protect pipes from corrosion. They provide a durable and chemically resistant layer.
- Polyethylene (PE) Coatings: PE coatings are applied to pipes for corrosion resistance and to provide a protective barrier against moisture and chemicals.
- Polypropylene (PP) Coatings: PP coatings are similar to PE coatings and are used to protect pipes in corrosive environments.
- Fusion-Bonded Epoxy (FBE): FBE coatings are applied using a heat treatment process to create a strong bond with the pipe surface, offering corrosion protection.
- Coal Tar Enamel (CTE): CTE coatings have been traditionally used for corrosion protection, although their use has decreased due to environmental concerns.
- Zinc Coatings: Zinc coatings, such as hot-dip galvanizing, are effective in preventing corrosion. They provide a sacrificial layer that corrodes instead of the pipe.
- Asphaltic Coatings: Bituminous coatings, made from asphalt or coal tar, offer protection against corrosion and are often used for underground pipelines.
- Concrete Coatings: Concrete can be applied as a coating for pipes, especially for those buried underground. It provides physical protection and can resist environmental conditions.
- Corrosion Inhibitors: Some pipes are coated with corrosion inhibitors that help prevent the corrosion of the pipe material.
The choice of coating material depends on factors such as the type of pipe, the environment in which it will be installed, and the specific requirements for corrosion protection.
Coating Thickness Guidelines
Asphaltic Coating
The USP-0550 pressure thickness guide specifies that the outside coating shall be an asphaltic coating approximately one mil thick.
Zinc Coating
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 8179-1 is the standard. 200 g/m2 is approximately 1 mil in thickness.
Paint Coating
One expert suggests that the range of thickness of paint on pipes is from 15 to 100 microns.
Plumbing Calculators
- Rolling Offsets (Run and Travel) – The Rolling Offset
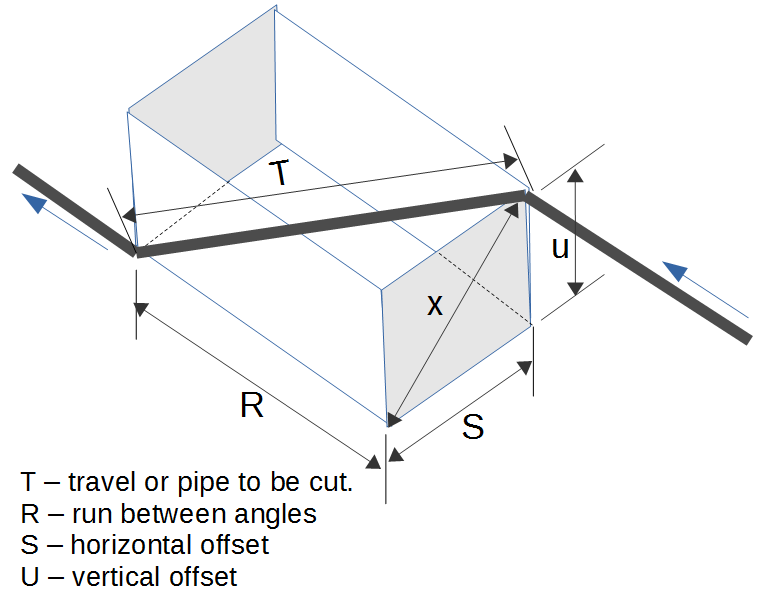 Rolling Offset Lengths
Rolling Offset Lengths Pipe Grading function computes the run and travel length a rolling offset based on the offsets and fittings. (see diagram).
- Pipe Grading - Compute the drop needed over a run to maintain a grade (e.g., 4" over 12')
- Diagonal of a Square - This is a simple calculation to assist in computing the diagonal of a square.
- Diagonal of a Box - This computes the length of the diagonal of a box (T) based on sides of length R, S and U.
- Flow Rate - This computes flow rate based on the total volume and the time it took to accumulate.
- Pipe Flow Volume - This computes the total volume from a pipe based on the flow rated and the duration of flow.
- Weight of Water in a Tank
- Computes the weight of water in a cylindrical tank based on the radius and height (or length).
- Weight of Water in a Pipe - Computes the weight of water or other substances in a pipe based on the dimension and material density.
- Weight of Sea Water in pipe - Computes the weight of sea water in a cylinder based on the radius and height (or length)
- Pressure Head - The Potential Gravity-Fed Water Pressure from a Tank (a.k.a. Pressure Head) based on the height of storage.
- Pipe Volume - Computes the volume in a pipe.
- Pipe Surface Area - Computes the surface area of a pipe.
- Pipe Coating Amount - Computes the volume of coating material for a pipe such as paint, polyethylene, polyurethane, zinc, bitumen, FBE or mortar.
- Volume of Water in a Tank (e.g. hot water tanks),
- Volume of a Spherical Container
- Weight of Water in a Spherical Container
- Volume of Water in Rectangular Tank
- Weight of Water in a Rectangular Tank
- Capillary Rise - The height of water in a small tube due to capillary force.
- Snow Water Equivalence - The volume of water created by an area and depth of snow.
- Pore Water Pressure - Pressure of uplift from the water table.
- Pipe Stress Budget - Computes the pressure that a pipe can withstand based on the allowable stress, wall thickness and outside diameter.
- Water in Basement Volume: Computes the volume of water in an area such as a basement based on the dimensions and the time required to pump it out based on a sump pump rate.
- Paint for Pipes: Computes the amount of paint needed to cover the exterior surface area of one or more pipes based on the pipe diameter, length, number of coats, number of pipes and the recommended area coverage of the paint.
- Time to Fill: Computes the amount of time necessary to fill something (e.g., tank or pool) based on the volume and flow rate.
- Pipe Insulation Calc: Computes the number of bags of pipe insulation needed for a run of pipes based on the 12' of length per bag and the length of pipe run to be insulated.
- Head Height: Computes the head height of liquid needed to achieve a pressure for a liquid (default is water).
Cable and Conduit Installation Calculators
- Electrical Metallic Tubing (EMT) Calculator: This provides the installation time and length estimates and the weight of EMT conduits.
- Galvanized Rigid Conduit (GRC) Calculator: This provides the installation time and length estimates and the weight of GRC conduits.
- PVC Schedule 40 Conduit Calculator: This provides the installation time, length and weight of PVC schedule 40 conduits.
- Metal Clad (MC) Cable Calculator: This provides the installation time, length and weight of metal clad (MC) cable.
- Fiber Optic Cable Loss Budget Calculator: Computes the acceptable dB loss in signal over a fiber-optic network based on the material type, number of connectors and splices and the overall length of the run.
- Voltage Drop Calculator: Computes the voltage drop over a length of cable and provides the needed gauge to keep voltage drop above a threshold.
- Telecommunications Calculator: This provide network and communications functions.
- Rolling Offset: Computes the run and travel distance in a rolling offset
The Coating Calculator has functions to compute the amounts of coating 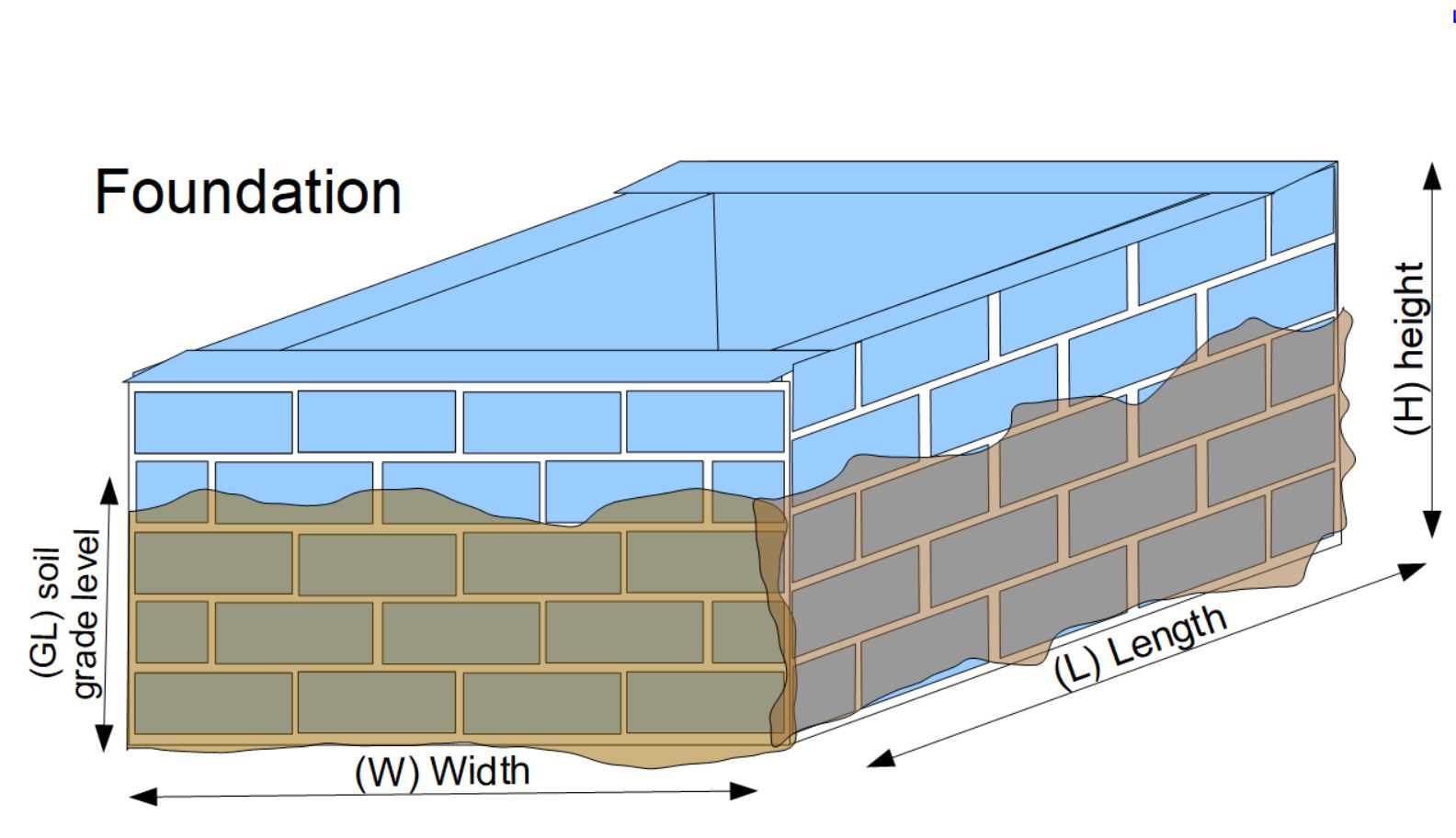 substance applied to a surface to protect, enhance, or provide specific properties. More than just paint, coatings can offer additional functionalities such as corrosion resistance, waterproofing, anti-fouling, thermal insulation, or electrical conductivity.
substance applied to a surface to protect, enhance, or provide specific properties. More than just paint, coatings can offer additional functionalities such as corrosion resistance, waterproofing, anti-fouling, thermal insulation, or electrical conductivity.
- Coating for a Foundation Wall: Computes the number of pails (5 gal) needed to coat a foundation wall based on the length and height.
- Concrete and Masonry Water-proofing: Computes the number of cans (1 gal) of concrete and masonry water-proofer needed to cover an area based on the width and height and number of coats.
- Corrugated Metal Panel Paint or Coating Volume: Computes the amount of paint or other coating (e.g., spray insulation) on an area of corrugated panels.
- Driveway Coating: Computes the number of pails (4.75 gal) needed to coat or seal a driveway. It provides a minimum and maximum number of pails and the surface area in square feet, all based on the length and width of the driveway.
- Foundation Coating: Computes the number of pails (5 gal) needed to coat all four walls of a foundation. It provides a minimum and maximum number of pails and the surface area of the foundation below grade in square feet, all based on the length, width and height of foundation below grade.
- Pipe Coating Amount: Computes the amount of coating material for the exterior surface area of a pipe based on the pipe diameter, length and the thickness of the coating.
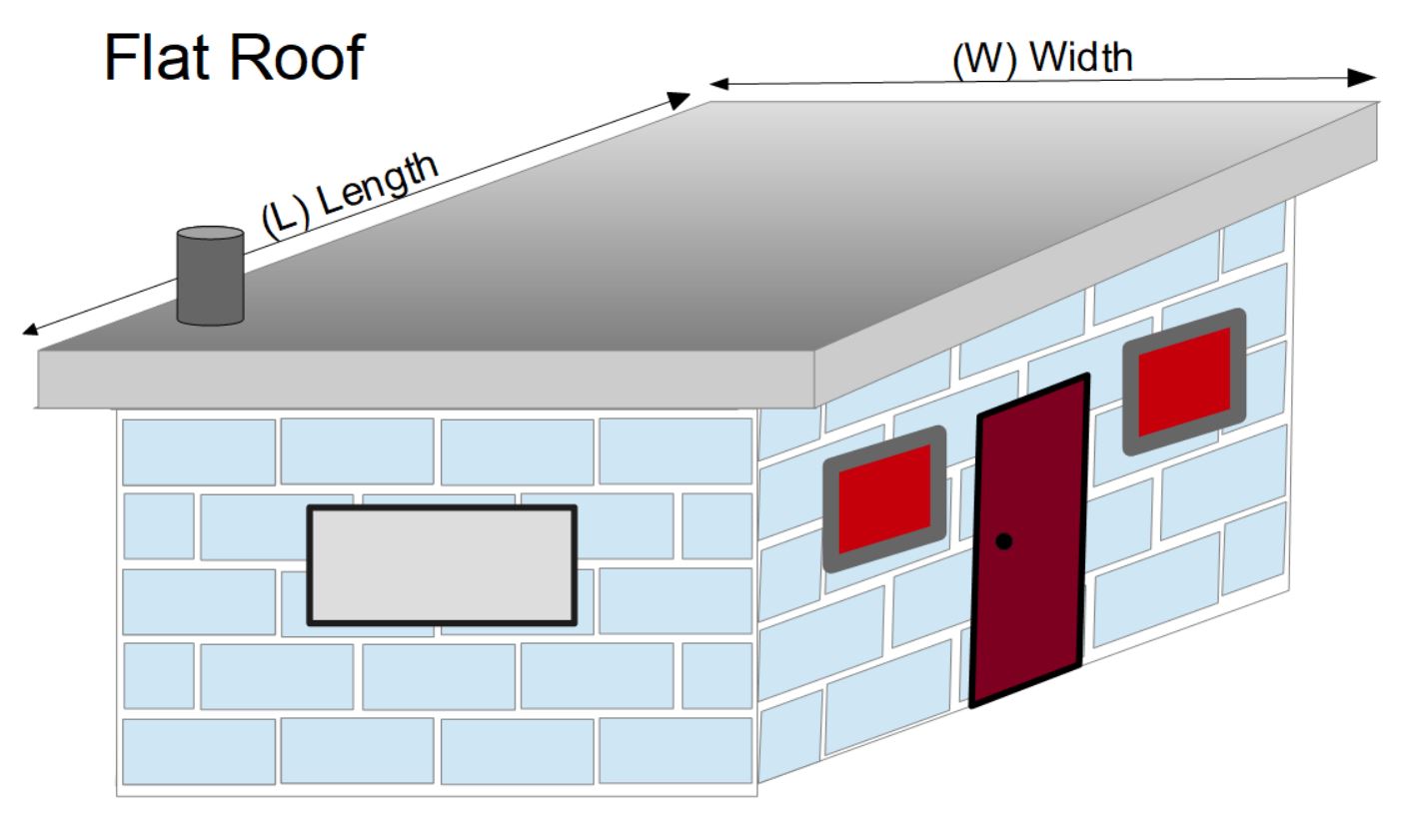
- Roof Coating: Computes the number of pails (e.g., 5 gal) needed to coat a flat roof.
 coating materials
coating materials 
