Scientific Calculator
The SciCalc contains a set of useful scientific calculator functions including the following:
Scientific Calculator Functions
Unit Conversions:
- Length or Distance: Converts an input length to compatible units.
- Area: Converts an input area to compatible units.
- Volume: Converts an input volume to compatible units.
- Velocity: Converts an input velocity to compatible units.
- Mass or Weight: Converts an input mass or weight to compatible units.
- Temperature: Converts and input temperature to compatible units.
- Force: Converts an input force to compatible units.
- Pressure: Converts an input pressure to compatible units.
Basic Math Functions:
- x-1: mathematical inverse or reciprocal of x, which is also 1/x
- x! : factorial of x
- x2: square of x
- x3: cube of x
- xy: x to the yth power
- 10x: ten to the xth power.
- √x: square root of x
- 3√x: cube root of x
- y√x: yth root of x
- Rand: Rreturns a random number between 0 and 1.
- log(x): base 10 log of x
- ln(x) : natural log of x
- MOD: integer remainder of x/y.
- GCD: greatest common divisor of two numbers
Math Constants:
- e - base of the natural log
- π - base of Euclidean geometry
Trigonometry Functions: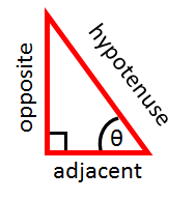
- sin(θ) : sine function of an angle.
- cos(θ): cosine function of an angle.
- tan(θ): tangent function of an angle.
- sin-1(x): angle from the inverse of a sine.
- cos-1(x): angle from the inverse of a cosine.
- tan-1(x): angle from the inverse of a tangent.
- sinh: Hyperbolic Sine
- sinh(x)=ex-e-x2
- cosh: Hyperbolic cosine
- cosh(x)=ex+ e-x2
- tanh: Hyperbolic tangent
- tanh(x)=sinh(x)cosh(x)=(ex-e-x)(ex+ e-x)
- coth: Hyperbolic cotangent
- coth(x)=1tanh(x)= (ex+e-x)(ex- e-x)
- csch: Hyperbolic cosecant
- csch(x)=1sinh(x)=2ex- e-x
- sech: Hyperbolic secant
- sech(x)=1cosh(x)=2ex+e-x
Inverse Hyperbolic Functions:
- arshinh: Arc Hyperbolic Sine
- arsinh(x) =ln(x+√x2+1) For: -∞<x<∞
- arcosh: Arc Hyperbolic Cosine
- arcosh(x)=ln(x+√x2-1) For: -∞<x<∞
- artanh: Arc Hyperbolic Tangent
- artanh(x)=12ln(1+x1-x) For: -1<x<1
- arcsch: Arc Hyperbolic Cosecant
- arcsch(x)=ln(1x+√1x2+1) For: -∞<x<∞,x≠0
- arsech: Arc Hyperbolic Secant
- arsech(x)=ln(1x+√1x2-1) For: 0<x≤1
- arcoth: Arc Hyperbolic Cotangent
- arcoth(x)=12⋅ln(x+1x-1) For: -∞<x<-1or1<x<∞
The Science
Hyperbolic trigonometric functions are a family of mathematical functions closely related to ordinary trigonometric functions. While ordinary trigonometric functions (like sine, cosine, and tangent) are defined based on the unit circle, hyperbolic trigonometric functions are defined based on the geometry of the hyperbola. These functions have properties similar to their ordinary trigonometric counterparts. For example, sinh(x) and cosh(x) are analogs of sine and cosine, respectively, and have similar symmetries and periodic properties. However, instead of describing the relationships between angles and sides of right triangles, hyperbolic trigonometric functions describe the relationships between sides and diagonals of hyperbolic triangles. They appear in various mathematical contexts, including differential equations, complex analysis, and geometry, as well as in physics and engineering.
Vector Calculator
3D vector arithmetic functions including Cartesian, Spherical and Cylindrical coordinate transforms.
- k V - scalar multiplication
- V / |V| - Computes the Unit Vector
- |V| - Computes the magnitude of a vector
- U + V - Vector addition
- U - V - Vector subtraction
- |U - V| - Distance between vector endpoints.
- |U + V| - Magnitude of vector sum.
- V • U - Computes the dot product of two vectors
- V x U - Computes the cross product of two vectors
- V x U • W - Computes the mixed product of three vectors
- Vector Angle - Computes the angle between two vectors
- Vector Area - Computes the area between two vectors
- Vector Projection - Compute the vector projection of V onto U.
- Vector Rotation - Compute the result vector after rotating around an axis.
- Normal to 3 Points - Vector Normal to a Plane Defined by Three Points
- (ρ, θ, φ) to (x,y,z) - Spherical to Cartesian coordinates
- (x,y,z) to (ρ, θ, φ) - Cartesian to Spherical coordinates
- (r, θ, z) to (x,y,z) - Cylindrical to Cartesian coordinates
- (x,y,z) to (r, θ, z) - Cartesian to Cylindrical coordinates
- Vector Components - Magnitude, Unit Vector and angle between vector and three coordinate axes
Statistics Calculator
- Observational Stats: This function accepts a table of numbers separated by commas and calculates observational statistics for any of the columns. This includes count, min, max, sum, sum of squares (Σx²), square of the sum (Σx)², mean, median, mode, range, mid point, rand, sort up, sort down, rand, population variance, population standard deviation, the sample/experimental variance, sample/experimental standard deviation.
- Frequency Distribution: This function lets you enter a string of numbers separated by commas, a low and high range and a number of bins. It then computes how many of the observations are in each of the bins between the high and low values designated.
- Random Sample (k): This generate a random sample of k items within a set.
- Percentile: This computes the relative percentile of an observation verses a set.
- P(A) = F / T: This computes the probability of a favorable event in a total number of outcomes.
- P(n,S) - Binomial Probability: Probability of S successes in n trials of a binomial distribution.
- Binomial Coefficient: from Pascal's Triangle.
- zSCORE (y in X): This computes the z SCORE of an observation in a set (X).
- zSCORE (y,μ,σ): This computes the z SCORE of an observation based on the mean and standard deviation.
- z from P(y): This computes the z SCORE based on a probability or percentile in a Normal Distribution table.
- P(y) left of z: This computes the percentile, probability or area under the curve of a Normal Distribution left of the z SCORE.
- P(y) right of z: This computes the percentile, probability or area under the curve of a Normal Distribution right of the z SCORE.
- Probability between z SCORES: This computes the area under the Normal Distribution curve between z SCOREs.
- Raw Score (P,μ,σ): This computes the raw score associated with a percentile in a Normal Distribution (μ,σ).
- Paired Sample t-test: This computes the various parameters associated with the Paired Sample t-test.
- y = a + bx: This is linear equation used with Linear Regression to predict values of Y.
- ANOVA (one way): The is one way analysis of variance
- (χ2) Chi-Square Test: This computes the Chi-Square value for an nxm array of data and provides the degrees of freedom.
- Linear Regression: This computes the regression line (least-squares) through a set of X and Y observations. It also computes the regression coefficient (r).
Quaternion Calculator
- Quaternion Addition
- Quaternion Subtraction
- Quaternion Multiplication
- Quaternion Magnitude
- Quaternion Versor
- Quaternion Conjugate
- Quaternion Inverse
- Quaternion of Rotation
- Vector Rotation
3x3 Matrix Characteristics: computes the determinant, trace, inverse and characteristic polynomial of a 3x3 matrix, Cramer’s Rule
Calculators and Collections
Equations
- Length Units Conversion KurtHeckman Use Equation
- Area Unit Conversion KurtHeckman Use Equation
- Volume Unit Conversion KurtHeckman Use Equation
- Velocity Unit Conversion KurtHeckman Use Equation
- Mass Unit Conversion KurtHeckman Use Equation
- Temperature Unit Conversion MichaelBartmess Use Equation
- Force Unit Conversion KurtHeckman Use Equation
- Pressure Units Conversion KurtHeckman Use Equation
- Reciprocal DavidC Use Equation
- Factorial KurtHeckman Use Equation
- Square DavidC Use Equation
- cube DavidC Use Equation
- Exponential DavidC Use Equation
- 10 to the x DavidC Use Equation
- Square Root DavidC Use Equation
- cube root DavidC Use Equation
- yth root DavidC Use Equation
- Random Real [0.0, 1.0] MichaelBartmess Use Equation
- Log_10 MichaelBartmess Use Equation
- ln DavidC Use Equation
- Modulus DavidC Use Equation
- Greatest Common Divisor DavidC Use Equation
- Sine DavidC Use Equation
- Cosine DavidC Use Equation
- Tangent MichaelBartmess Use Equation
- Arcsine KurtHeckman Use Equation
- Arccosine KurtHeckman Use Equation
- Arctangent KurtHeckman Use Equation
- Hyperbolic Sine MichaelBartmess Use Equation
- Hyperbolic Cosine KurtHeckman Use Equation
- Hyperbolic Tangent KurtHeckman Use Equation
- Hyperbolic Cotangent KurtHeckman Use Equation
- Hyperbolic Cosecant KurtHeckman Use Equation
- Hyperbolic Secant KurtHeckman Use Equation
- Arc Hyperbolic Sine KurtHeckman Use Equation
- Arc Hyperbolic Cosine KurtHeckman Use Equation
- Arc Hyperbolic Tangent KurtHeckman Use Equation
- Arc Hyperbolic Cosecant KurtHeckman Use Equation
- Arc Hyperbolic Secant KurtHeckman Use Equation
- Arc Hyperbolic Cotangent KurtHeckman Use Equation
Data Items
- Eulers Number MichaelBartmess Use Data Item
- π MichaelBartmess Use Data Item
- Comments
- Attachments
- Stats
No comments |

