Plumbing Calculator
Plumbing Calculators
- Rolling Offsets (Run and Travel) – The Rolling Offset
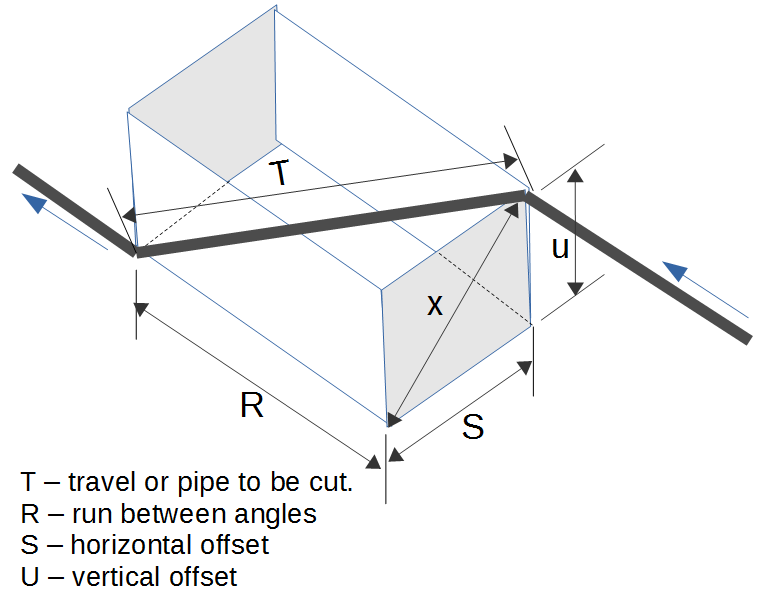 Rolling Offset Lengths
Rolling Offset Lengths Pipe Grading function computes the run and travel length a rolling offset based on the offsets and fittings. (see diagram).
- Pipe Grading - Compute the drop needed over a run to maintain a grade (e.g., 4" over 12')
- Diagonal of a Square - This is a simple calculation to assist in computing the diagonal of a square.
- Diagonal of a Box - This computes the length of the diagonal of a box (T) based on sides of length R, S and U.
- Flow Rate - This computes flow rate based on the total volume and the time it took to accumulate.
- Pipe Flow Volume - This computes the total volume from a pipe based on the flow rated and the duration of flow.
- Weight of Water in a Tank
- Computes the weight of water in a cylindrical tank based on the radius and height (or length).
- Weight of Water in a Pipe - Computes the weight of water or other substances in a pipe based on the dimension and material density.
- Weight of Sea Water in pipe - Computes the weight of sea water in a cylinder based on the radius and height (or length)
- Pressure Head - The Potential Gravity-Fed Water Pressure from a Tank (a.k.a. Pressure Head) based on the height of storage.
- Pipe Volume - Computes the volume in a pipe.
- Pipe Surface Area - Computes the surface area of a pipe.
- Pipe Coating Amount - Computes the volume of coating material for a pipe such as paint, polyethylene, polyurethane, zinc, bitumen, FBE or mortar.
- Volume of Water in a Tank (e.g. hot water tanks),
- Volume of a Spherical Container
- Weight of Water in a Spherical Container
- Volume of Water in Rectangular Tank
- Weight of Water in a Rectangular Tank
- Capillary Rise - The height of water in a small tube due to capillary force.
- Snow Water Equivalence - The volume of water created by an area and depth of snow.
- Pore Water Pressure - Pressure of uplift from the water table.
- Pipe Stress Budget - Computes the pressure that a pipe can withstand based on the allowable stress, wall thickness and outside diameter.
- Water in Basement Volume: Computes the volume of water in an area such as a basement based on the dimensions and the time required to pump it out based on a sump pump rate.
- Paint for Pipes: Computes the amount of paint needed to cover the exterior surface area of one or more pipes based on the pipe diameter, length, number of coats, number of pipes and the recommended area coverage of the paint.
- Time to Fill: Computes the amount of time necessary to fill something (e.g., tank or pool) based on the volume and flow rate.
- Pipe Insulation Calc: Computes the number of bags of pipe insulation needed for a run of pipes based on the 12' of length per bag and the length of pipe run to be insulated.
- Head Height: Computes the head height of liquid needed to achieve a pressure for a liquid (default is water).
Weight of Plumbing Contents
One can estimate the weight of the contents of a pipe or tank by computing the volume of the container and then multiplying the volume by the mean density of the contents. The most common content of plumbing is water. However, pipes and tanks often contain other materials. The following information provides an estimated density of many materials for calculating convenience. Please reference authoritative sources before relying on the accuracy of the following data with regard to risking life, health or wealth.
| Common Mean Densities |
|
Natural
Food
Industrial
Fuels
|
Mean Density of Fluids
Mean density is the average amount of mass within a volume for a substance. Note, volume of a material is often highly subject to the temperatures, since materials expand as they warm. For that reason, mean densities of substances are often cited with a set of nominal conditions such as temperature and barometric pressure.
The formula for mean density is:
μD = V / m
where:
- μD = mean density
- V = Volume in units like gallons or liters
- m = Mass in units like kilograms or pounds
Mean density is also often indicated as the Greek symbol rho (ρ).
The mean density of fluids can be useful since fluids (liquids and gases) conform to the shape of their containers. This is why it is possible to use the mean density of a substance and the dimensions of its container to estimate the weight/mass of the substance in the container.
Equations
- Rolling Offset KurtHeckman Use Equation
- Pipe Drop KurtHeckman Use Equation
- Diagonal of a Square MichaelBartmess Use Equation
- Box Diagonal KurtHeckman Use Equation
- Flow Rate KurtHeckman Use Equation
- Pipe Flow Volume KurtHeckman Use Equation
- Weight of Water in a Tank KurtHeckman Use Equation
- Weight of Water in a Pipe KurtHeckman Use Equation
- Weight of Sea Water in a pipe KurtHeckman Use Equation
- Pressure Head KurtHeckman Use Equation
- Pipe Volume KurtHeckman Use Equation
- Pipe Surface Area vCollections Use Equation
- Pipe Coating Amount KurtHeckman Use Equation
- Volume of Water in a Tank KurtHeckman Use Equation
- Sphere Tank Volume KurtHeckman Use Equation
- Weight of Fluid in Spherical Container KurtHeckman Use Equation
- Volume of Water in Rectangular Tank KurtHeckman Use Equation
- Weight of Water in Rectangular Tank KurtHeckman Use Equation
- Capillary Rise MichaelBartmess Use Equation
- Snow Water Equivalent (SWE) Titan Use Equation
- Pore Water Pressure Anastase Use Equation
- Pipe Stress Budget KurtHeckman Use Equation
- Water in Basement Volume KurtHeckman Use Equation
- Paint for Pipes KurtHeckman Use Equation
- Time to Fill KurtHeckman Use Equation
- Pipe Insulation Calc KurtHeckman Use Equation
- Head Height KurtHeckman Use Equation
Wikiclips
- Comments
- Attachments
- Stats
No comments |

